Recently, Proofpoint Targeted Attack Protection Mobile Defense discovered apps on iOS devices – that is, iPhones and iPads – that did not match apps in the Apple App Store. MDM assessments showed that these devices were not jailbroken.
In the course of further analysis, Proofpoint’s security research team discovered a rogue app store that allows iOS device users to download apps from a catalog claiming 1 million apps onto their iPhones or iPads without jailbreaking the devices. The rogue app store even allows paid apps to be downloaded for free.
This analysis focuses on vShare, a rogue app marketplace that has existed for several years serving apps for use on Android devices and on jailbroken iOS devices. vShare has now found a way to enable their store for non-jailbroken iOS devices. We have named this type of rogue app store “DarkSideLoader.”
What is the danger?
The ability to download iOS apps to non-jailbroken iOS devices from a DarkSideLoader marketplace places consumers and corporate employers at risk. These apps can make use of private iOS APIs to access operating system functions that would not be permitted by apps that have been vetted by Apple for publishing on the official app store. These apps could also use known or zero-day security vulnerabilities that could lead to devices being jailbroken or granting administrator privileges to these illegitimate apps.
The example of Android apps demonstrates the potential of this threat. Proofpoint researchers have studied both the Android and iOS app marketplace that is accessed by the vShare DarkSideLoader marketplace app. On Android, we have found attempts to root devices, install apps without user permission, and communicate to known malicious sites on the Internet.
Circumventing the official Apple app store vetting process makes it possible to download apps that could act as Remote Access Trojans, allowing attackers access to mobile devices of employees when they are active on internal corporate networks. While researchers have previously documented instances of rogue app stores targeting non-jailbroken iOS devices, these marketplaces appeared to be only accessible to devices accessing them from a Chinese IP address. [1] The vShare marketplace is noteworthy in that it is accessible to iOS devices connecting from anywhere in the world, representing a global expansion of this attack technique.
This technique also makes it possible to load onto the iOS devices configuration profiles that would allow an attacker to configure VPN settings to redirect network traffic to their man-in-the-middle nodes, as well as change various OS settings (Fig. 1)
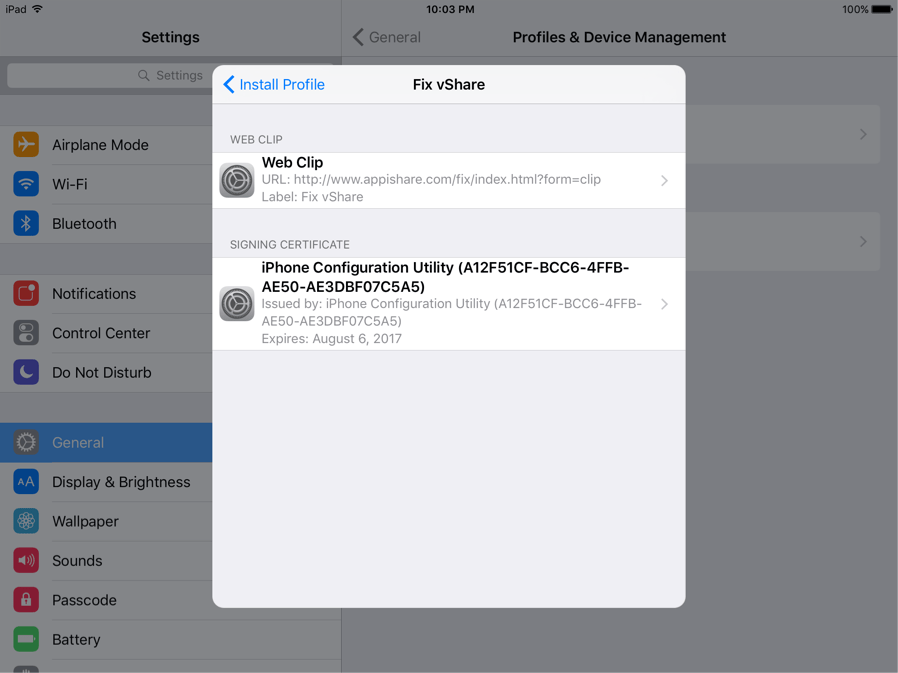
Figure 1: An iPhone configuration profile that is installed by vshare app marketplace
What is sideloading?
Sideloading is the process of downloading and installing apps onto a mobile device from a source that is not an official consumer app store or a valid enterprise app store. On Android devices this can be done by enabling the settings to download apps from unknown sources in the general device settings.
On iOS devices installing unapproved apps was previously only possible by jailbreaking an iPhone or iPad. However, the DarkSideLoader technique allows sideloading of apps through the use of a fraudulent or stolen enterprise app distribution certificate coupled with app re-signing.
How is it possible to create and operate a DarkSideLoader app store?
On Android, downloading apps from unofficial apps stores simply requires that these app stores request that the user enable the ability to download apps from stores other than Google Play.
On iOS the DarkSideLoader technique is more sophisticated. In this example the vShare app is downloaded onto a user’s device by clicking on a link on the vshare[.]com website. This downloads the com.appvv[.]vshare app onto the user’s iOS device. The app has been signed with an Enterprise App distribution certificate, issued by Apple. These certificates are normally issued to enterprises that want to operate their own internal app stores for employees. Clicking on a link on a website hosting links to the malicious app store downloads a DarkSideLoader app (Fig. 2). In iOS 7 and 8, when the user clicks on the app to run it, they are asked if they want to trust the publisher (Fig. 3).
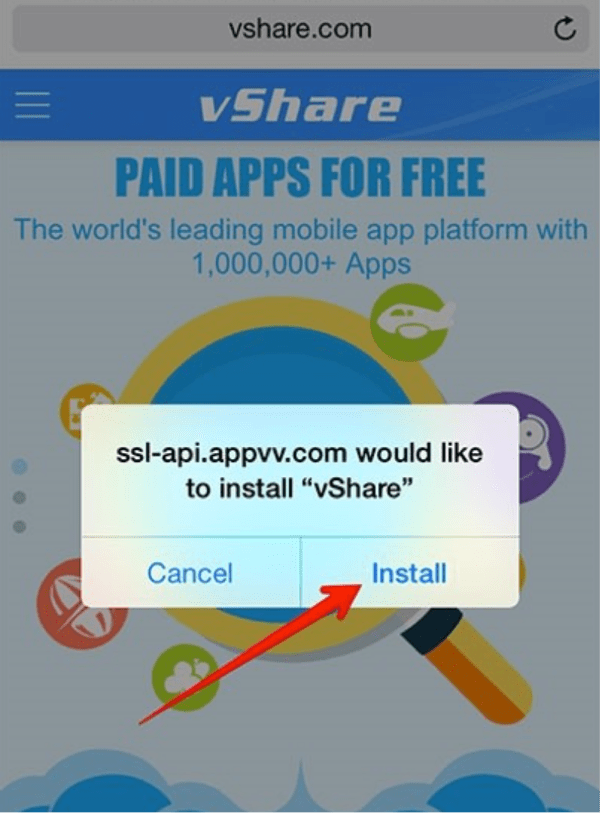
Figure 2: Installing the vShare downloader app
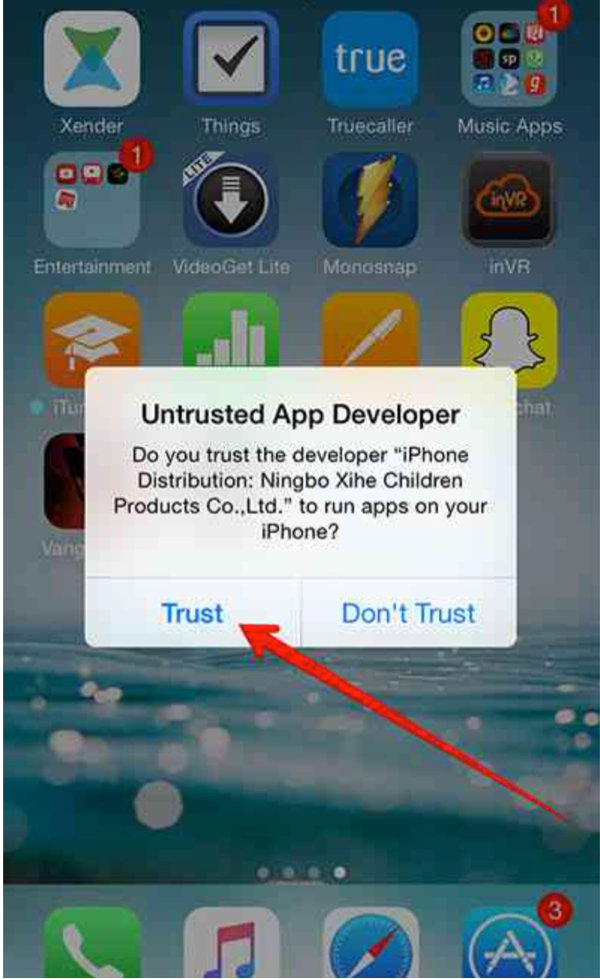
Figure 3: Notification dialog to trust the vShare downloader app
After clicking “Trust”, the downloaded app runs. An enterprise certificate will be installed and trusted on the device, allowing the app to run in iOS. The app can also download other apps.
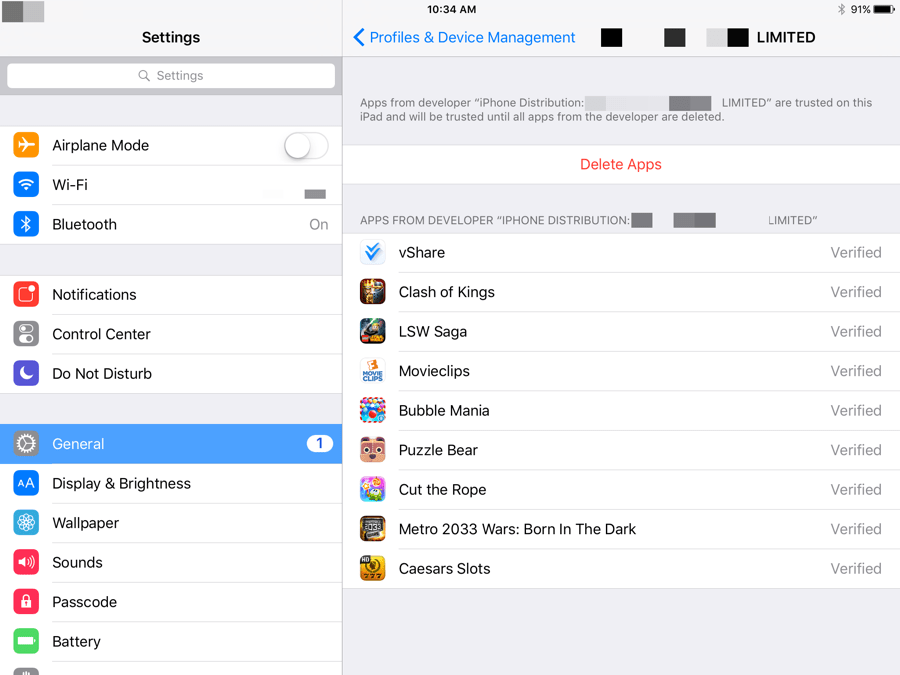
Figure 4: An enterprise app distribution certificate and the apps that have been installed on an iPad from the rogue marketplace under this certificate
On iOS 9, clicking on the app will not bring up the Trust button. Rather the user must open the Settings app on the iOS device, and click on Profiles. From there they click on the publisher name and select Trust. From then onward, the DarkSideLoader marketplace app is enabled and can download any apps that it desires onto the user’s device.
Recognizing that iOS puts up greater barriers to accidentally downloading apps from DarkSideLoader stores, the rogue app marketplaces provide helpful and easy-to-follow guidance on how to do make the necessary trust settings changes (Fig. 5-7).
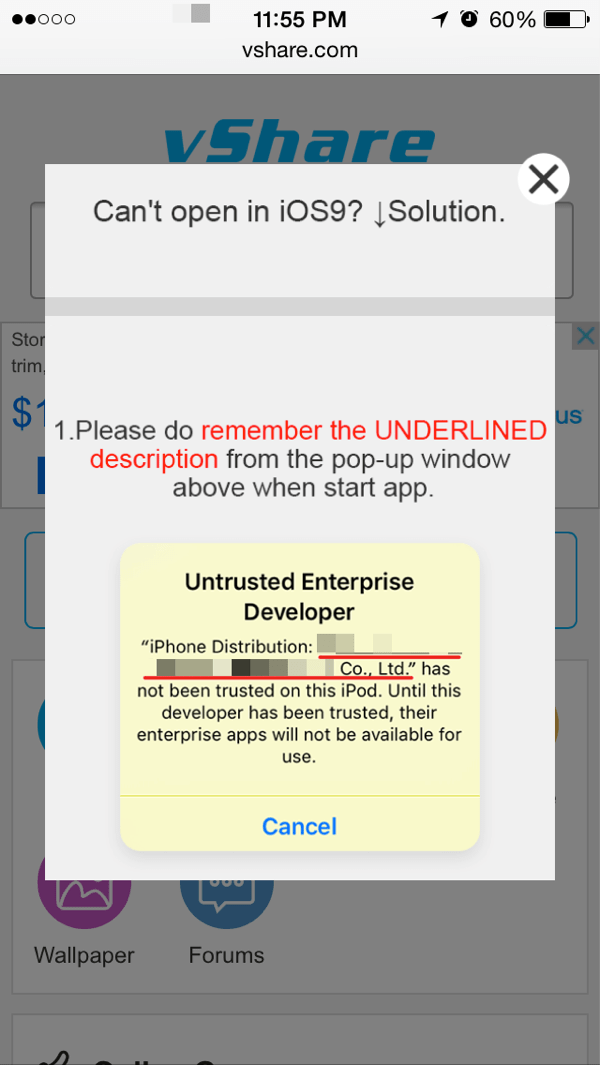
Figure 5: Instructions to end-user for enabling trust of apps from unofficial app stores
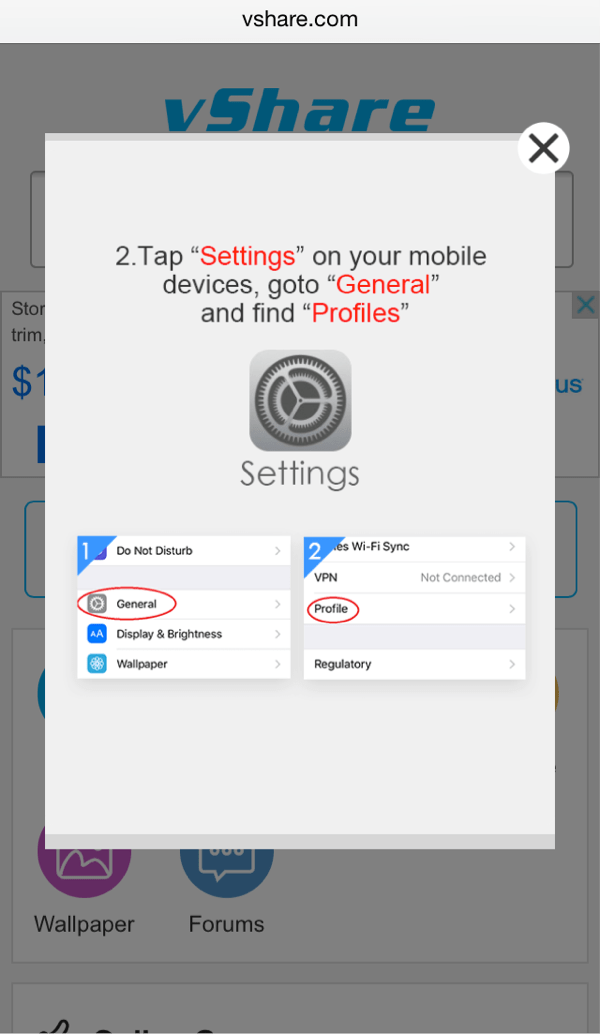
Figure 6: Instructions to end-user for enabling trust of apps from unofficial app stores
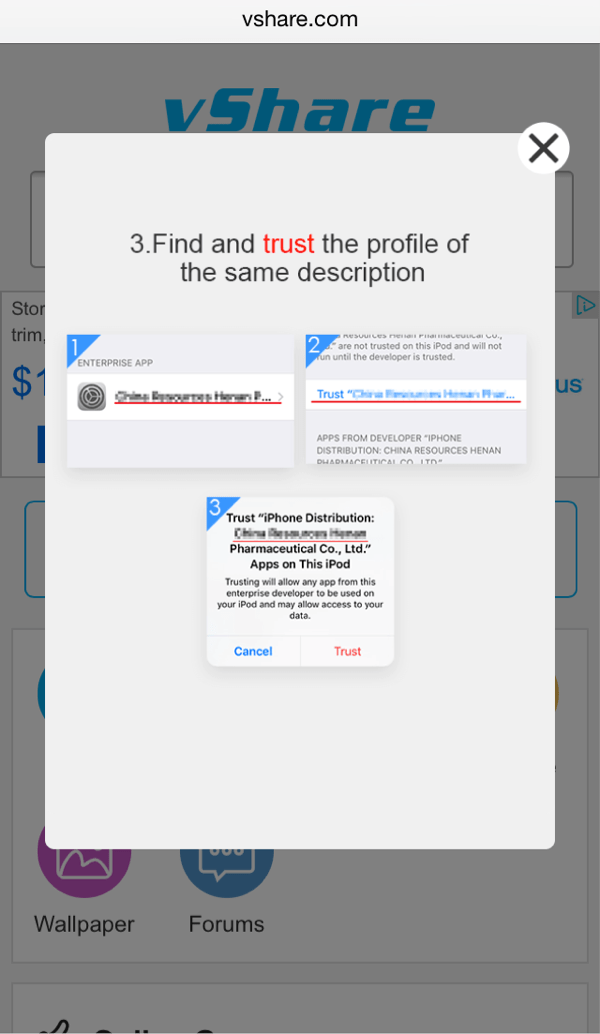
Figure 7: Instructions to end-user for enabling trust of apps from unofficial app stores
When the user chooses to download an app from a DarkSideLoader marketplace, the marketplace app downloads the selected illegitimate app to the phone. The marketplace digitally re-signs the app with the enterprise app distribution certificate. Because that enterprise is trusted on the iOS device, those apps will run just like an app downloaded from the legitimate Apple app store.
A rogue app marketplace using the DarkSideLoader technique has implemented a large scale app re-signing capability. Legitimate games and other apps are decrypted, modified, and re-signed with an enterprise certificate for download by users of the rogue app marketplace.
Figure 8 shows the contents of a vShare marketplace app to a non-jailbroken iOS device (Fig. 8).
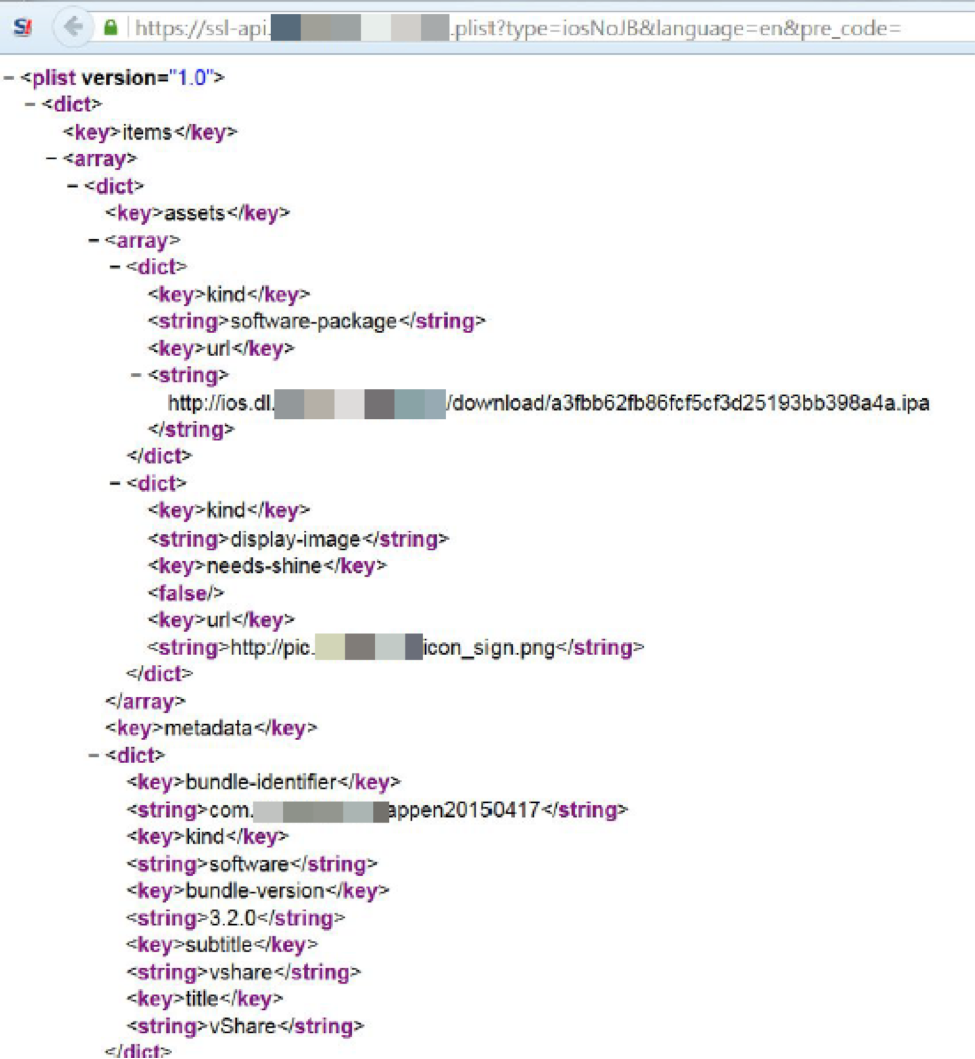
Figure 8: Downloaded content for vShare marketplace app
Why would someone use a DarkSideLoader marketplace?
If these marketplaces pose such a risk, why would anyone consider downloading apps from them? Experience with Android apps shows that users, or their children, may choose to access a rogue app marketplace in order to download games, wallpaper and other media without paying for them. They can also access apps that give them access to streamed movies and other content, and productivity apps without payment. There are also apps available that are not available on the legitimate Apple app store, such as for pirating content and downloading BitTorrent files.
The vShare marketplace claims 1M apps are available. Proofpoint has found over 15,000 iOS apps available through this DarkSideLoader site, compared to over 400,000 apps available on their Android side loading service. The site claims over 40M users, and Proofpoint investigations indicate that approximately 25 percent of the users are on iOS devices.
Offering free downloads of popular, paid apps represents an attractive lure to draw people to a DarkSideLoader marketplace and entice them to click. The top-ten paid apps on the Apple App Store are all available for free on the vShare marketplace, including well-known titles such as Minecraft and Geometry Dash. Other popular paid iOS apps offered as free downloads by this market include games such as Grand Theft Auto: San Andreas and Clash of Clans, as well as business productivity apps from publishers including Adobe and Microsoft and apps for pirating movies such as MovieBox.
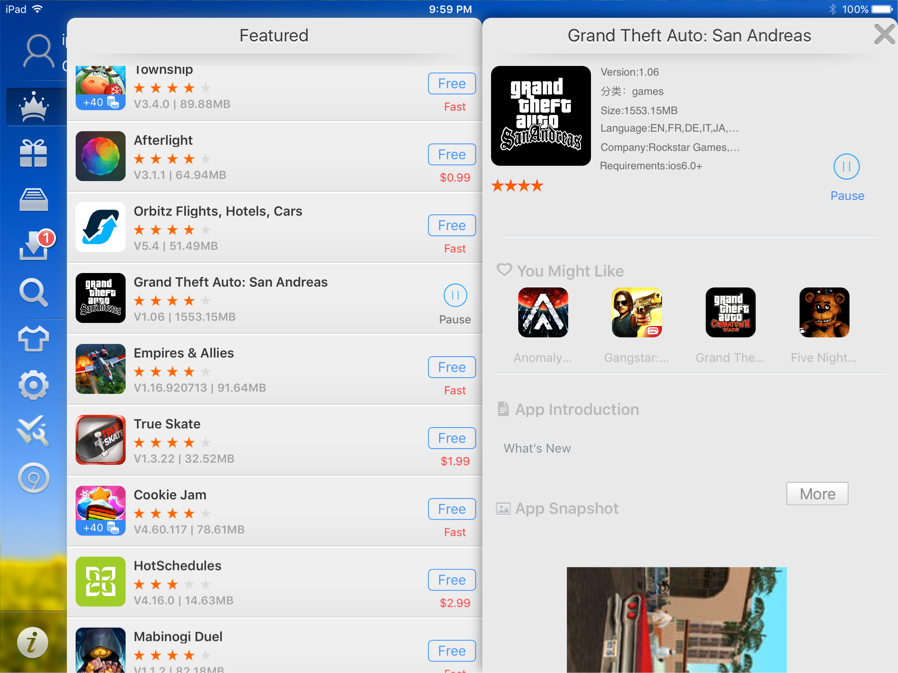
Figure 9: Apps available from rogue app marketplace
Users who access these markets may think that they are safe to download these apps because their mobile devices are not jailbroken and the apps appear to come from reputable publishers. What they do not realize is that these apps could be designed or modified to include malicious code. Apps from rogue marketplaces can access private OS API’s or could exploit known or zero-day vulnerabilities in the operating system to take over control of their device.
Fraudulent enterprise app certificates and DarkSideLoader marketplaces
There are several ways that rogue marketplaces can obtain an enterprise app distribution certificate.
- Fraudulently obtain a certificate by creating a fake company. Apple vets requests to obtain an enterprise app distribution certificate by reviewing a company’s request, verifying email and phone contacts, and by charging a $299 fee to a credit card. Operators of DarkSideLoader marketplaces can create a convincing fake company and use a stolen credit card to get a certificate issued. They will need to have a phone number and email address.
- Fraudulently obtain a certificate by imitating a real company. In this attack, the operator uses the website information of an existing company to pretend to be an employee of that company, and get Apple to issue an enterprise iOS developer account and enterprise app distribution certificate. Stolen credit cards can be used to pay the issuance fee. By imitating a real company, the attackers can use substantiating information such as a Dun & Bradstreet number to create a convincing request.
- Steal a certificate from a company that has one. In this attack the operator phishes the apple developer website credentials of a company that creates legitimate iOS apps. There are hundreds of thousands of legitimate iOS app developers. When the attacker has the login credentials of an app developer, they can log into their account and either request a new enterprise app distribution certificate, or download a copy of one that already exists.
Several enterprise app certificates are being used by the vShare app marketplace.
Previous analysis shows that certificates have typically been from Chinese companies; however, new research shows that fraudulent certificates are now being attributed to companies in other countries.
When a new DarkSideLoader marketplace is found, Apple revokes the enterprise app distribution certificate. This will prevent new users from downloading the marketplace app and subsequent illegitimate apps. Over a period of weeks as iOS devices check certificate revocation lists, the illegitimate apps that they have downloaded will cease to function and they will have to re-download them.
However, we have seen that rogue marketplace operators are able to obtain multiple enterprise app distribution certificates. For example, the vShare marketplace has used numerous certificates in recent months; when these were no longer valid, new ones replaced them. (See IOC’s at the end of this post for a list of certificate registrants observed in this investigation.)
Business drivers for rogue app marketplaces
There is a simple reason why rogue app marketplaces exist and are now making it easy for people to download free apps and content using DarkSideLoader techniques: money. These app stores make money by showing advertisements to users. One such service is VEarnDollar.
Another option could be for these stores to embed malicious code, such as remote access Trojans, into otherwise legitimate apps and sell that access to attackers who want to infiltrate enterprises or government agencies. In fact, analysis of the vShare marketplace for Android has already shown apps trying to root devices and install other apps without permission.
Since 2011 they have operated in marketplaces distributing apps for jailbroken and rooted devices. The ability to offer app downloads to non-jailbroken devices through enterprise signing certificates substantially expands their marketplace presence.
The marketplace domain has been registered for more than seven years, but traded among owners. The current owners have been on this domain since October 14, 2015. We believe that the domain was transferred to a Chinese intermediary in May 2014. This intermediary waited over one year before transferring the domain to the current operators of an active DarkSideLoading marketplace in mid-October 2015.
The person who is listed as the contact for vshare[.]com has 1,055 domains registered. The vshare[.]com domain itself has changed IP addresses 17 times in 2015.
Summary and recommendations
A survey of Proofpoint’s ten largest US enterprises using TAP Mobile Defense in the week of December 18, 2015 found that 40 percent had employees who were actively using a DarkSideLoader-enabled rogue app marketplace.
In short, consumers should not trust or use rogue app marketplaces, even with non-jailbroken iOS devices. Enterprises should deploy purpose-built solutions that can detect the presence of apps from DarkSideLoader marketplaces. Scanning the legitimacy of apps, looking for rogue app marketplace downloaders, and scanning for known DarkSideLoader enterprise certificates are the most effect means of limiting the potential impact of rogue apps in enterprise environments.
References
Indicators of Compromise:
Proofpoint has observed certificates being used by the following:
Limitless Holdings-2 Limited
Jiangxi Installation Engineering Co, LTD
Fujian Zhengton Electronic Technology Co, Ltd
Ningbo Xihe Children Products Co., Ltd
HOF & Co DMCC
Popular paid apps available for free on the vShare marketplace
Top 10 paid apps on Apple App Store are all available for free on vShare rogue app store (as of Dec 22, 2015):
| App Name | Publisher |
| Minecraft: Pocket Edition | Mojang |
| Heads Up! | Warner Bros |
| Cut the Rope: Magic | ZeptoLab UK Limited |
| NBA 2K16 | 2K |
| Geometry Dash | RobTop Games AB |
| Mineraft: Story Mode | Telltale Inc |
| Scribblenauts Unlimited | Warner Bros |
| Toca Blocks | Toca Boca AB |
| Lucky Block for Minecraft | JK2Designs LLC |
| Terraria | 505 Games |
Other notable popular paid apps that are also on vShare for free:
| App Name | Publisher |
| Clash of Clans | Supercell |
| Spotify Music | Spotify |
| Candy Crush Saga | King.com Limited |
| Madden NFL Mobile | Electronic Arts |
| Grand Theft Auto: San Andrea | Rockstar Games |
| Plague Inc | Ndemic Creations |
| Facetune | Lightricks Ltd |
Top paid business apps available for free:
| App Name | Publisher |
| Docs To Go Premium | DataViz, Inc |
| Scanner Pro | Readdle |
| Splashtop 2 remote desktop | Splashtop Inc. |
| PDF Office | Readdle |
| Printer Pro | Readdle |
Subscribe to the Proofpoint Blog

