
Business email compromised (BEC) attacks have seen an explosive 476% growth between Q4 2017 and Q4 2018, while the number of email fraud attempts against companies increased 226% QoQ.
BEC attacks use social engineering to target specific company employees, regularly from the firm’s Finance department, and try to persuade them into wiring large sums of money to third-party banking accounts controlled by the attackers.
Threat actors to not use malicious URLs or attachments with their BEC campaigns, therefore this type of attack can be a lot harder to spot by the targeted employees, especially when they do not have the training to detect them.
Proofpoint’s Quarterly Threat Report for Q4 2018 says that “On average, companies targeted by BEC received about 120 fraudulent emails in the fourth quarter of the year, up from 36 in Q3 2018 and up from 21 in the year-ago quarter.”
To make BEC operations even more successful, email fraud actors will also spoof the targeted company’s domain to make sure that nothing looks out of place when the target opens and reads the attack message.
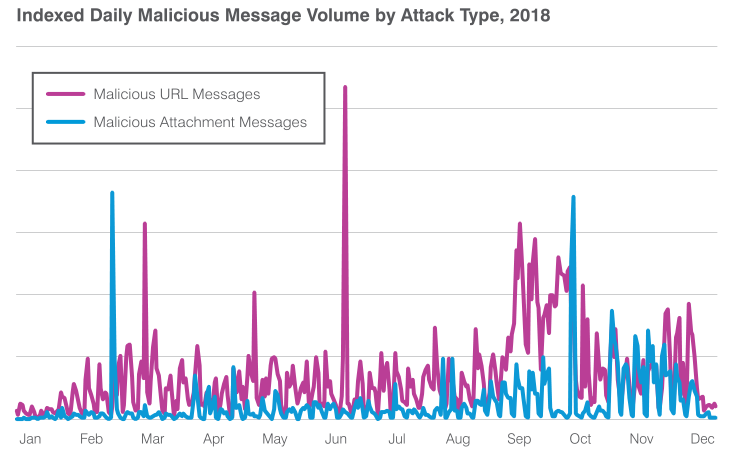
Proofpoint’s researchers also found that “Messages leveraging malicious URLs outnumbered malicious attachments by roughly 2:1 for Q4 and 3:1 for the entire year.”
The switch to a “many-to-many” assault technique made BEC campaigns even more dangerous during 2018. This method allows fraudsters to take cover under multiple spoofed identities to go for a larger number of targets within the same organization.
Proofpoint’s findings match the ones of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) from July 2018, which said that “The BEC/EAC scam continues to grow and evolve, targeting small, medium, and large business and personal transactions. Between December 2016 and May 2018, there was a 136% increase in identified global exposed losses. The scam has been reported in all 50 states and in 150 countries.”
Digital Shadows’ threat researchers also found “12.5 million company email inboxes and 33,000 finance department credentials” of numerous enterprises exposed to unauthorized access, with exactly 27,992 (83%) of them also having a password.
As BEC mitigation measures, Digital Shadows recommends configuring cloud accounts and Internet-facing storage devices correctly, BEC training for company employees, adding at least one level of manual controls to all wire transfers, as well as keeping an eye out for exposed company e-mail credentials.
Proofpoint Quarterly Threat Report's key findings:
EMAIL:
• Banking Trojans remain the top email-borne threat in Q4, making up 56% of all malicious payloads in Q4; Emotet comprised 76% of all banking Trojan payloads.
• Remote access Trojans accounted for 8.4% of all malicious payloads in Q4 and 5.2% for the year, marking a significant change from previous years in which they were rarely used by crimeware actors.
• Ransomware dropped even further in Q4 to just one tenth of 1% of overall malicious message volume.
• Malicious messages bearing credential stealers or downloaders collectively jumped more than 230% year over year
• Email fraud, also known as BEC, continued its dramatic growth. The number of email fraud attacks against targeted companies increased 226% QoQ and 476% vs. Q4 2017.
WEB-BASED ATTACKS:
• Coinhive activity spiked to 23 times the average for the year for two weeks in December; overall, Coinhive activity continued to grow slowly aside from this spike.
• In Q4, we still observed a 150% increase in social engineering detections on our worldwide network of IDS sensors; while this is a slower growth rate than observed in previous quarters, it continues to demonstrate a trend towards social engineering even as EK activity has remained low.
SOCIAL MEDIA:
• Fraudulent social media support account phishing, or ”angler phishing,” has increased 442% year-over-year
• Phishing links on social channels continue to drop as platforms address this issue algorithmically

.jpg)
Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now