Table of Contents
Email security remains a critical challenge for all types of organisations and institutions, with domain spoofing and phishing attacks becoming increasingly sophisticated. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) stands as the only widely deployed technology that makes the sender’s “From” address trustworthy in email communications.
Recent data shows the urgency of implementing effective email security and authentication, as DMARC adoption has doubled in the past year, with 110,000 new domains implementing it monthly. This authentication protocol is a crucial defence mechanism, allowing organisations to protect their domains from unauthorised use while providing detailed reporting on email authentication results.
Cybersecurity Education and Training Begins Here
Here’s how your free trial works:
- Meet with our cybersecurity experts to assess your environment and identify your threat risk exposure
- Within 24 hours and minimal configuration, we’ll deploy our solutions for 30 days
- Experience our technology in action!
- Receive report outlining your security vulnerabilities to help you take immediate action against cybersecurity attacks
Fill out this form to request a meeting with our cybersecurity experts.
Thank you for your submission.
DMARC Definition
DMARC, which stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance, is an open email authentication protocol that provides domain-level protection of the email channel. DMARC authentication detects and prevents email spoofing techniques used in phishing, business email compromise (BEC), and other email-based attacks.
Building on existing standards—Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)—DMARC is a critical and widely deployed technology that validates the header “From” domain authenticity. The domain owner can publish a DMARC record in the Domain Name System (DNS) and create a policy to tell receivers what to do with emails that fail authentication.
Identity-based attacks, such as business email compromise (BEC), often evade traditional defences. Download our solution brief.
With DMARC, domain owners can effectively outline their authentication practices and determine specific actions that can be taken when an email fails authentication. This powerful email authentication protocol helps domain owners combat a host of security threats.
Examples
- Domain spoofing: An attacker spoofs a company’s domain to make an email seem legitimate.
- Email spoofing: A term for spoofing activities involving email.
- Business email compromise (BEC): An email that appears to come from a senior employee within an organisation requesting that money or sensitive information be sent.
- Impostor email: A spoofed email sent by an impostor claiming to be someone they are not.
- Email phishing: An email attempting to get victims to install malware or offer their credentials. A phishing email often looks like a familiar brand to appear legitimate.
- Consumer phishing: Spoofed email sent to a consumer of a company claiming to be from that company intending to steal credentials.
- Partner spoofing: Business-based spoofed email between supply chain partners requesting to change payment details to siphon money.
- Whaling email scam: Fraudulent email sent to a senior employee within an organisation aiming to get a large financial gain.
- AI-enhanced phishing: Sophisticated phishing attempts using AI-generated content to create more convincing and personalised fraudulent emails.
Standards
- Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC): An email validation system that detects and prevents email spoofing. It helps combat certain techniques often used in phishing and email spam, such as emails with forged sender addresses that appear to come from legitimate organisations.
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF): An email validation protocol that detects and blocks emails. It allows receiving mail exchangers to verify that incoming mail from a domain comes from an IP address authorised by its administrators.
- DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): An email authentication method that detects email spoofing. It allows the receiver to check that an email claiming to come from a specific domain was authorised by its owner.
- M3AAWG sender best practices: Industry guidelines that outline email authentication requirements, including DMARC implementation, for bulk senders to maintain deliverability and security.
- Google-Yahoo 2024 requirements: New authentication standards requiring DMARC implementation for bulk senders (>5,000 emails daily) to maintain inbox deliverability.
SPF and DKIM
SPF and DKIM are the two primary authentication mechanisms that play a crucial role in DMARC. Each is based on unique records that help confirm the legitimacy of emails.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email validation protocol that allows an organisation to specify who can send emails from their domains. Organisations can authorise senders within an SPF record published in the Domain Name System (DNS). This record includes the approved IP addresses of email senders, including the IP addresses of service providers authorised to send emails on the organisation’s behalf. While SPF alone has limitations due to email forwarding and the complexity of modern email infrastructure, publishing and checking SPF records is a reliable way to stop phishing and other email-based threats that forge “From” addresses and domains.
Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication protocol that allows the receiver to check that an email from a specific domain was authorised by its owner. It enables an organisation to take responsibility for transmitting a message by attaching a digital signature. Verification is done through cryptographic authentication using the signer’s public key published in the DNS. DKIM signatures should use at least 2048-bit keys, as shorter keys are considered cryptographically weak. The signature ensures that parts of the email have not been modified since the digital signature was attached.
Both SPF and DKIM help establish email authenticity and prevent common email security threats, like spoofing and phishing attacks. In the context of DMARC, these authentication mechanisms are used in conjunction to validate the sender’s identity. Major email providers now require both SPF and DKIM authentication for bulk senders.
The DMARC policy, published as a DNS record, instructs recipient servers on how to handle emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks. By combining SPF and DKIM results with a DMARC policy, domain owners can specify whether to quarantine or reject emails that fail authentication, allowing better control over email delivery and reducing the risk of fraudulent emails attempting to hijack their domain name.
Learn how Proofpoint Hosted SPF simplifies DNS management and improves reliability for SPF-based authentication.
What Is a DMARC Record?
A DMARC record is a special text entry (known as a DNS TXT record) that lives in your domain’s DNS settings, acting like a set of instructions for receiving mail servers. This record, which appears under “_dmarc.yourdomain.com”, contains specific tag-value pairs that define authentication policies and reporting preferences for incoming emails claiming to be from your domain.
The record consists of essential components, with the most critical being the version tag (v=DMARC1), policy tag (p=none/quarantine/reject), and reporting address tag (rua=mailto:example@domain.com). These elements work together to help organisations verify legitimate email sources and protect their domains from unauthorised use, providing a robust framework for email authentication.
DMARC is a key building block of a broader anti-impersonation strategy. Proofpoint Impersonation Protection provides AI-driven detection of display name deception, lookalike domains, and supplier fraud, complementing your DMARC policy for stronger defence.
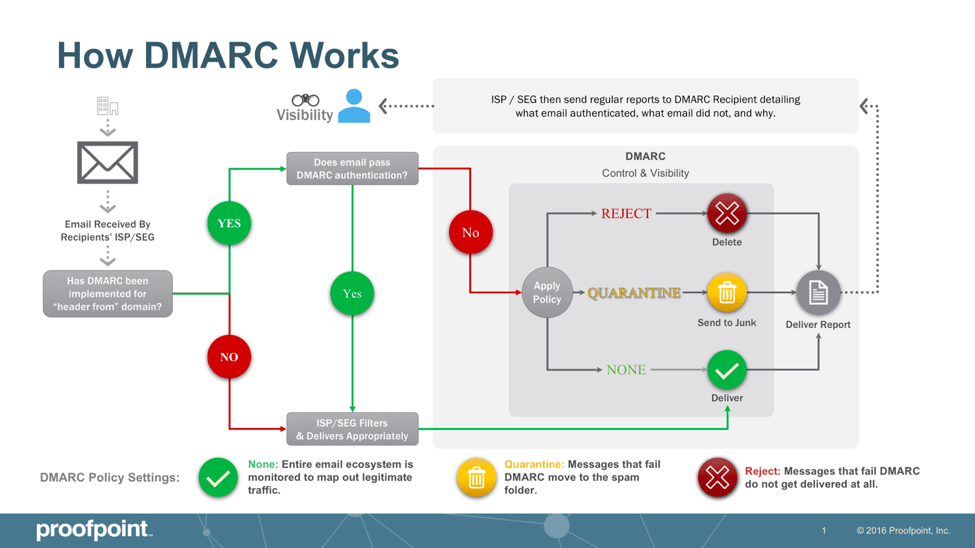
How DMARC Works
For a message to pass DMARC authentication, it must pass SPF authentication and SPF alignment and/or pass DKIM authentication and DKIM alignment. If a message fails DMARC, senders can instruct receivers on what to do with that message per a DMARC policy. There are three DMARC policies the domain owner can enforce: none (the message is delivered to the recipient, and the DMARC report is sent to the domain owner), quarantine (the message is moved to a quarantine folder), and reject (the message is not delivered at all).
While starting with a “none” policy is recommended, the domain owner receives DMARC reports to help ensure that all legitimate emails are identified and pass authentication. Organisations should plan to progress beyond “none” within 12 months of implementation. Once the domain owner is confident they have identified all legitimate senders and have fixed authentication issues, they can move to a policy of “reject” and block phishing, business email compromise, and other email fraud attacks. As an email receiver, an organisation can ensure that its secure email gateway enforces the DMARC policy implemented by the domain owner. This will protect employees against inbound email threats.
SPF authentication starts by identifying all legitimate IP addresses that should send emails from a given domain and then publishes this list in the DNS. Due to DNS lookup limits, organisations should carefully manage their SPF records and consider using include mechanisms. Before delivering a message, email providers verify the SPF record by looking up the domain included in the “envelope from” address within the hidden technical header of the email. If the IP address sending an email on behalf of this domain is not listed in the domain’s SPF record, the message fails SPF authentication.
For DKIM authentication, the sender first identifies what fields they want to include in their DKIM signature, such as the “From” address, the body of the email, the subject, and more. These fields must remain unchanged in transit, or the message will fail DKIM authentication. The sender’s email platform will create a hash of the text fields included in the DKIM signature. Once the hash string is generated, it is encrypted with a private key only the sender can access. After the email is sent, it’s up to the email gateway or consumer mailbox provider to validate the DKIM signature by locating a public key that matches the private key. Then, the DKIM signature is decrypted back to its original hash string.
DMARC Requirements
Major email providers have implemented new authentication requirements in 2024 to enhance email security and reduce fraudulent activities. These requirements primarily affect bulk email senders.
Google and Yahoo Requirements
Organisations sending over 5,000 emails daily to Gmail or Yahoo accounts must implement:
- A DMARC record with a minimum policy of “p=none”
- SPF and DKIM records for each sending domain
- SPF or DKIM alignment for the “From” header
- ARC authentication for forwarded messages
- One-click unsubscribe functionality for commercial messages (by June 1, 2024)
- Spam rates below 0.3%, as reported in Postmaster Tools
Enforcement Timeline
The implementation process follows a graduated schedule:
- February 2024: Initial enforcement began with temporary errors for non-compliant traffic
- April 2024: Google starts rejecting a percentage of non-compliant email traffic
- June 2024: Full enforcement of DMARC requirements and one-click unsubscribe functionality
Additional Requirements
Organisations must also:
- Segregate email class types by domain
- Adhere to SMTP “tempfailure” and rejection errors
- Maintain proper email authentication setup to prevent messages from being marked as spam or rejected
These requirements represent a significant shift in email authentication standards, making DMARC implementation no longer optional but a business necessity for maintaining effective email deliverability.
Benefits of DMARC
DMARC provides several benefits in reinforcing email-based cybersecurity measures for organisations that implement it. Some of the core advantages of leveraging DMARC include:
- Ensures email deliverability: Setting a DMARC record in your DNS settings is now required for overall email deliverability and preventing threat actors from delivering malicious emails using your domain.
- Lowers the risk of email phishing attacks: DMARC effectively prevents and mitigates the risk of phishing attacks, which can be costly to an organisation and its bottom line.
- Enforces sender policies: DMARC allows organisations to enforce policies via its DNS record, defining specific practices for email authentication and providing instructions for receiving mail servers about how to enforce them.
- Protects brand reputation: DMARC helps protect an organisation’s brand reputation by preventing cyber criminals from impersonating their domain and deceiving customers and clients into releasing sensitive information.
- Provides thorough authentication reporting: DMARC checks provide visibility into an organisation’s email system by offering comprehensive authentication reporting and threat intelligence.
- Functions at scale: DMARC is intended to perform with internet scalability, making it an effective tool for large-scale organisations, institutions, and corporate entities.
- Meets compliance requirements: DMARC implementation helps organisations comply with modern email security standards and industry requirements from major providers like Google and Yahoo.
While many of these benefits overlap, the underlying function of DMARC is to better protect email through effective authentication and threat mitigation.
Email that passes authentication is more likely to reach inboxes. Want to improve your sender reputation and reach?
DMARC Best Practices and Tools
Due to the volume of DMARC reports that an email sender can receive and the lack of clarity provided within DMARC reports, fully implementing DMARC authentication can be challenging. These tools and best practices can help ensure your organisation optimises DMARC.
- Publish policies to your DNS record that clearly define your organisation’s practices for email authentication and document instructions for receiving mail servers about how to enforce those policies.
- Use automated DMARC monitoring and analysis tools to process aggregate (RUA) and forensic (RUF) reports effectively.
- Additional data and insights beyond what’s included within DMARC reports help organisations identify email senders faster and more accurately. This helps speed up the implementation of DMARC authentication and reduces the risk of blocking legitimate emails.
- Professional service consultants with DMARC expertise can help organisations with DMARC implementation. Consultants help identify all legitimate senders, fix authentication issues, and even work with email service providers to ensure they authenticate properly.
- Organisations can create a DMARC record in minutes and start gaining visibility through DMARC reports by enforcing a DMARC policy of “none”. However, they should establish a clear timeline for moving to stricter policies.
- After identifying all legitimate email senders—including third-party email service providers—and fixing any authentication issues, organisations should progress to quarantine policy before finally enforcing a DMARC policy of “reject”.
- Implement strong SPF records with minimal DNS lookups and DKIM with 2048-bit keys as foundational steps.
DMARC implementation can be complicated, but it’s a critical protocol in securing your organisation’s email channels and mitigating fraudulent activity.
How to Create a DMARC Record
Implementing DMARC is now essential to protect your email against impostors and fraudulent activity. Creating a DMARC record is the first step to protecting your organisation, customers, and brand reputation from email fraud. You can use Proofpoint’s DMARC Creation Wizard to create a record for your organisation or follow the steps below to get started.
DMARC records are hosted on your DNS servers as TXT entries. Every host provider grants DNS access to customers, so you can add this TXT entry from the registrar where the domain was registered or in a dashboard provided by the website host. The steps to create a DMARC record differ based on the registrar or host, but creating the record is the same for every domain. After you authenticate into your host or registrar, create a DNS entry using the following steps:
- Create a TXT record. After you start the creation process, you must enter a name and value for the record.
- Name your record “DMARC”. In some host configurations, the domain name is automatically appended to the name. If it is not added automatically, name the record _dmarc.yourdomain.com.
- Enter the value for your record. Here’s a recommended initial DMARC record: v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:youraddress@yourdomain.com; ruf=mailto:forensics@yourdomain.com; pct=100
The key values in the entry are critical for direction when users send emails to your domain. The first “v” value is necessary and defines the version. This value will be the same for all records. The second “p” value determines what happens when the email passes or fails. In this example, the value is set to “none”, indicating nothing will happen. This value is recommended initially to ensure that DMARC works correctly before quarantining messages.
After you verify that DMARC works correctly, the “p” value can be changed to “quarantine” or “reject”. Start with “none” for at least 30 days, then move to “quarantine” for another 30 days before considering “reject”. The message will be set aside until you review it. The “reject” option will outright drop records that don’t pass DMARC rules. The “pct” tag allows you to apply the policy gradually, though most organisations should maintain it at 100%. Only use the “reject” option when you are positive that no important messages will be dropped by your DMARC settings.
DMARC Policies
DMARC offers three distinct policy levels that determine how receiving mail servers handle emails that fail authentication. Each policy is designated by the “p=” tag in the DMARC record, providing different levels of protection and control.
P=none Policy
This monitoring-only policy allows organisations to gain visibility into email streams without affecting delivery. While emails undergo authentication checks, they continue to flow normally regardless of the results. This policy serves as a crucial first step in DMARC implementation, though it provides no actual protection against domain spoofing.
P=quarantine Policy
The quarantine policy instructs receiving servers to treat suspicious emails with increased scrutiny. When an email fails DMARC authentication, it is typically directed to the recipient’s spam folder rather than the primary inbox. This provides a middle-ground approach, allowing legitimate emails that might fail authentication to remain accessible while flagging potential threats.
P=reject Policy
As the strictest DMARC policy, reject tells receiving servers to block any emails that fail authentication completely. These messages never reach the recipient’s inbox or spam folder, offering the strongest protection against email spoofing and domain abuse. Recent data indicates that while p=none remains the most common policy, organisations should consider moving toward stricter enforcement, as nearly 75% of senders using p=none have no plans to upgrade their policies despite increasing security requirements.
To simplify and accelerate deployment, download our Proofpoint Verified DMARC data sheet.
DMARC Myths and Misconceptions
Email authentication can be complex, and several persistent myths about DMARC continue to circulate among security professionals and business leaders. Here are the most significant misconceptions that need clarification:
- DMARC is just a spam filter: DMARC doesn’t function as a traditional spam filter. Instead, it provides specific instructions to receiving mail servers about how to handle emails sent from your domain.
- Only large organisations need DMARC: Every organisation with a public domain needs DMARC protection, regardless of size. Cyber criminals target businesses of all scales, making authentication essential for everyone.
- P=none provides protection: While p=none is a necessary starting point, it only enables monitoring and provides no actual protection against spoofing. Organisations must progress to quarantine or reject policies for genuine security benefits.
- DMARC stops all email attacks: While DMARC is crucial for email security, it doesn’t prevent all types of attacks. For example, it cannot stop lookalike domain spoofing, which is why organisations need a layered security approach.
- DMARC is a quick fix: Implementing DMARC requires a methodical approach. Organisations must start by monitoring and analysing results and gradually progress through policy levels. Rushing to enforce strict policies immediately can disrupt legitimate email flow.
- Parked domains don’t need DMARC: Every domain, even those not actively sending emails, requires DMARC protection. Attackers can spoof any domain, making universal protection necessary.
- DMARC is purely a security project: DMARC implementation is actually a cross-functional initiative requiring collaboration between IT, security, compliance, and marketing teams to be truly effective.
Download our Getting Started with DMARC White Paper to understand the foundational steps and avoid common pitfalls.
DMARC vs. DKIM
DMARC and DKIM (or DomainKeys Identified Mail) are email authentication protocols that help organisations fight email compromise and impersonation attacks. However, DMARC is more robust in implementing policies and utilising reporting mechanisms. While both protocols use public key cryptography, DMARC and DKIM use different methods to validate email flow. DKIM is solely an authentication method, while DMARC generates aggregate reports to help optimise an organisation’s email strategy.
DMARC aligns both SPF and DKIM mechanisms to provide reporting across activities performed under those two policies. DMARC requires at least one of these mechanisms to pass authentication and alignment checks. This enables domain owners to publish policies in their DNS records specifying how to check the “From:” field presented to end-users and how the receiver should deal with failures. Under current requirements from major email providers, both DKIM and DMARC are necessary components of a complete email authentication strategy.
DKIM’s purpose is to verify whether an email is legitimate, while DMARC provides explicit instructions about what to do with an illegitimate email.
Organisations that fully implement DMARC not only reduce fraud but also improve email deliverability. Read our DMARC & Deliverability eBook to learn how authentication improves inbox placement and builds brand trust.
Why Use DMARC for Email?
DMARC has become a mandatory requirement of an organisation’s email security strategy, as it allows recipients of emails using the authenticated domain to trust that messages came from the domain owner and not an impostor. In turn, organisations use DMARC for these core purposes:
- Security: DMARC helps prevent phishing scams from infiltrating an organisation’s network, which can compromise its security.
- Visibility: Administrators can monitor emails sent using your domain to ensure they are properly authenticated using SPF and/or DKIM.
- Brand Protection: DMARC can block spoofed messages that might damage your brand’s reputation.
- Deliverability: Major email providers now require DMARC implementation for bulk senders to ensure reliable inbox placement.
- Compliance: DMARC helps organisations meet evolving security standards and regulatory requirements.
DMARC provides a way for domain owners to specify their own authentication practices and determine the actions taken when an email fails to meet authentication criteria. By implementing DMARC-compliant email, organisations can secure their domain(s) from unauthorised use and protect against daily email security threats.
How Proofpoint Can Help
Proofpoint offers services and resources to help organisations implement and maintain DMARC records. Here are some ways Proofpoint can help with DMARC:
- Leverage Proofpoint’s verified DMARC check to identify domain owners who have properly implemented and successfully maintained the domains’ DMARC infrastructure.
- Implement and monitor a DMARC record for your organisation with Proofpoint’s comprehensive email authentication solution. This is essential for leveraging DMARC to better authenticate and protect your email and its users.
- Use documentation from Proofpoint on how to effectively implement DMARC. Follow this DMARC technical brief and the simple steps included within.
- Access Proofpoint’s automated DMARC monitoring and reporting tools to simplify implementation and maintenance.
- Leverage Proofpoint’s expertise to meet new sender requirements from major email providers.
Proofpoint emphasises the importance of DMARC in protecting against email-based attacks such as phishing and business email compromise (BEC). By implementing DMARC, organisations can gain visibility into who is sending emails on their behalf and distinguish between legitimate and malicious senders. Contact Proofpoint to learn more.











