Key Takeaways
-
Proofpoint is tracking multiple different threat clusters that use similar themes related to fake browser updates.
-
Fake browser updates abuse end user trust with compromised websites and a lure customized to the user's browser to legitimize the update and fool users into clicking.
-
Threat actors do not send emails to share the compromised websites. The threat is only in the browser and can be initiated by a click from a legitimate and expected email, social media site, search engine query, or even just navigating to the compromised site.
-
The different campaigns use similar lures, but different payloads. It is important to identify which campaign and malware cluster the threat belongs to help guide defender response.
Overview
Proofpoint is currently tracking at least four distinct threat clusters that use fake browser updates to distribute malware. Fake browser updates refer to compromised websites that display what appears to be a notification from the browser developer such as Chrome, Firefox, or Edge, informing them that their browser software needs to be updated. When a user clicks on the link, they do not download a legitimate browser update but rather harmful malware.
Based on our research, TA569 has used fake browser updates for over five years to deliver SocGholish malware, but recently other threat actors have been copying the lure theme. Each threat actor uses their own methods to deliver the lure and payload, but the theme takes advantage of the same social engineering tactics. The use of fake browser updates is unique because it abuses the trust end users place in both their browser and the known sites that they visit.
Threat actors that control the fake browser updates use JavaScript or HTML injected code that directs traffic to a domain they control, which can potentially overwrite the webpage with a browser update lure specific to the web browser that the potential victim uses. A malicious payload will then automatically download, or the user will receive a prompt to download a “browser update,” which will deliver the payload.
Fake browser update lure and effectiveness
The fake browser update lures are effective because threat actors are using an end-user's security training against them. In security awareness training, users are told to only accept updates or click on links from known and trusted sites, or individuals, and to verify sites are legitimate. The fake browser updates abuse this training because they compromise trusted sites and use JavaScript requests to quietly make checks in the background and overwrite the existing, website with a browser update lure. To an end user, it still appears to be the same website they were intending to visit and is now asking them to update their browser.
Proofpoint has not identified threat actors directly sending emails containing malicious links, but, due to the nature of the threat, compromised URLs are observed in email traffic in a variety of ways. They are seen in normal email traffic by regular end users who are unaware of the compromised websites, in monitoring emails such as Google alerts, or in mass automated email campaigns like those distributing newsletters. This creates a situation where these emails are considered to be malicious during the time the site is compromised. Organizations should not treat the fake browser update threats as only an email problem, as end users could visit the site from another source, such as a search engine, social media site, or simply navigate to the site directly and receive the lure and potentially download the malicious payload.
Each campaign uniquely filters traffic to hide from researchers and delay discovery, but all the methods are effective at filtering. While this may reduce the potential spread of malicious payloads, it enables actors to maintain their access to the compromised sites for longer periods of time. This can complicate the response, because with the multiple campaigns and changing payloads, responders must take time to figure out what they need to look for and identify the relevant indicators of compromise (IOCs) at the time of the download.
Campaigns
The current landscape includes four different threat clusters using unique campaigns to deliver fake browser update lures. Due to the similarity in the lures and attack chain, some public reporting has incorrectly attributed the activity to the same threat cluster. Based on Proofpoint's distinct visibility, Proofpoint researchers were able to break these into more granular clusters.
Proofpoint’s research focuses on the fake browser update landscape overall, to provide details on how defenders can identify each unique campaign, as well as additional links to additional Proofpoint or third-party reporting containing in-depth research and analysis. For example, Jérôme Segura of Malwarebytes has put together a good resource showing some of the images each campaign uses as lures on GitHub.
Each campaign has some general shared characteristics that can be described as three distinct stages of the campaign. “Stage 1” is a malicious injection on a legitimate, but compromised, website. “Stage 2” refers to the traffic to and from the actor-controlled domain that does most of the filtering and hosts the lure and malicious payload. “Stage 3” is the execution of the payload on a host after download.
SocGholish
SocGholish is the primary threat that people think of when talking about a fake browser update lure and it has been well documented over the years. Proofpoint typically attributes SocGholish campaigns to a threat actor known as TA569. Proofpoint has observed TA569 act as a distributor for other threat actors.
Currently, TA569 is using three different methods to direct traffic from the stage 1 compromised websites to their actor-controlled stage 2 shadowed domains.
The first method is using an injection that utilizes the Keitaro traffic distribution system (TDS) via a variety of actor-controlled domains. Those domains will filter some requests out before routing to the stage 2 domains. Most of the injects that point to Keitaro TDS URLs will contain multiple different redirect domains in the same file, as seen in figure 2 below.
The second method TA569 uses is Parrot TDS (also known as NDSW/NDSX) to obfuscate their injected code and apply similar filtering before routing requests to the stage 2 domains. Compromised websites may contain as many as 10 malicious JavaScript files that all contain Parrot TDS injections leading to SocGholish payloads.
The third method TA569 uses is a simple JavaScript asynchronous script request in compromised websites’ HTML that reaches out to a stage 2 domain.
The variety of injections make it difficult for defenders to both identify the location of the malicious injection and reproduce the traffic due to the various stages of filtering.
Each of these methods reaches out to a stage 2 domain which does additional filtering and will deliver the fake browser update lure and payload to traffic that passes the filtering. The payload can be either a plain JavaScript (.js) file, usually named “Update.js”, or a zipped JavaScript file. If the payload is executed by the user, it will first fingerprint the host via wscript. Depending on the results of the fingerprinting, the JavaScript will either quit, load a remote access trojan (RAT), or wait for further commands from the threat actor, which has been reported leading to Cobalt Strike or BLISTER Loader. Proofpoint has recently observed SocGholish infections leading to AsyncRAT and NetSupport RAT as the RAT payloads.
Figure 1. SocGholish fake update lure spoofing a Chrome update.
Figure 2. Keitaro TDS inject example.
Figure 3. Parrot (NDSW) inject example.
Figure 4. Asynchronous inject example.
RogueRaticate/FakeSG
The second fake browser update our researchers identified is known as RogueRaticate or FakeSG. Proofpoint first identified this activity in May 2023, and third-party researchers dubbed it a copy of the existing and high-volume SocGholish campaigns. The activity may have started in the wild as early as November 2022. Proofpoint does not attribute the RogueRaticate activity to a tracked threat actor at this time, and it has consistently been distinctly differentiated from SocGholish campaigns.
RogueRaticate injects heavily obfuscated JavaScript code into existing JavaScript files on stage 1 websites. The injected JavaScript reaches out to a stage 2 domain. The stage 2 domain hosts a Keitaro TDS that filters out unwanted requests and responds with a blank “body” value in a JSON response. When it identifies a target to receive the lure, it sends the lure double Base64 encoded in the “body” value. The lure contains a button which, if pressed, uses an HTML href attribute to download the payload from a separate compromised site, typically hosted on WordPress.
The fake update payload for the RogueRaticate campaigns has always involved an HTML Application (.hta) file. The HTA is either zipped or downloaded via a shortcut (.url) file that points to the .lnk. The .hta file typically loads a malicious NetSupport RAT payload onto the host via the same stage 2 domain that hosted the malicious payload.
Figure 5. Example RogueRaticate fake update lure spoofing a Chrome update.
Figure 6. Example RogueRaticate inject.
ZPHP/SmartApeSG
Proofpoint first identified another new cluster of fake update campaigns leading to NetSupport RAT in June 2023. The activity was first publicly reported by Trellix in August 2023. This activity has been referred to as ZPHP by Proofpoint or SmartApeSG in public documentation. The inject is a simple script object that is added into a compromised website’s HTML code. It makes an asynchronous request to either “/cdn/wds.min.php” or “/cdn-js/wds.min.php” on a stage 2 domain. The response is heavily obfuscated JavaScript code that will attempt to create an iframe and make a second request to “/zwewmrqqgqnaww.php?reqtime=<epoch time>” which appears to filter out undesired requests and return the browser update lure to non-filtered requests. The payload is downloaded via a base64 encoded zip file.
The zipped browser update payload usually contains a JavaScript (.js) file that will load a malicious NetSupport RAT payload onto the host. Proofpoint has also seen the .zip contain an executable (.exe) that loaded Lumma Stealer.
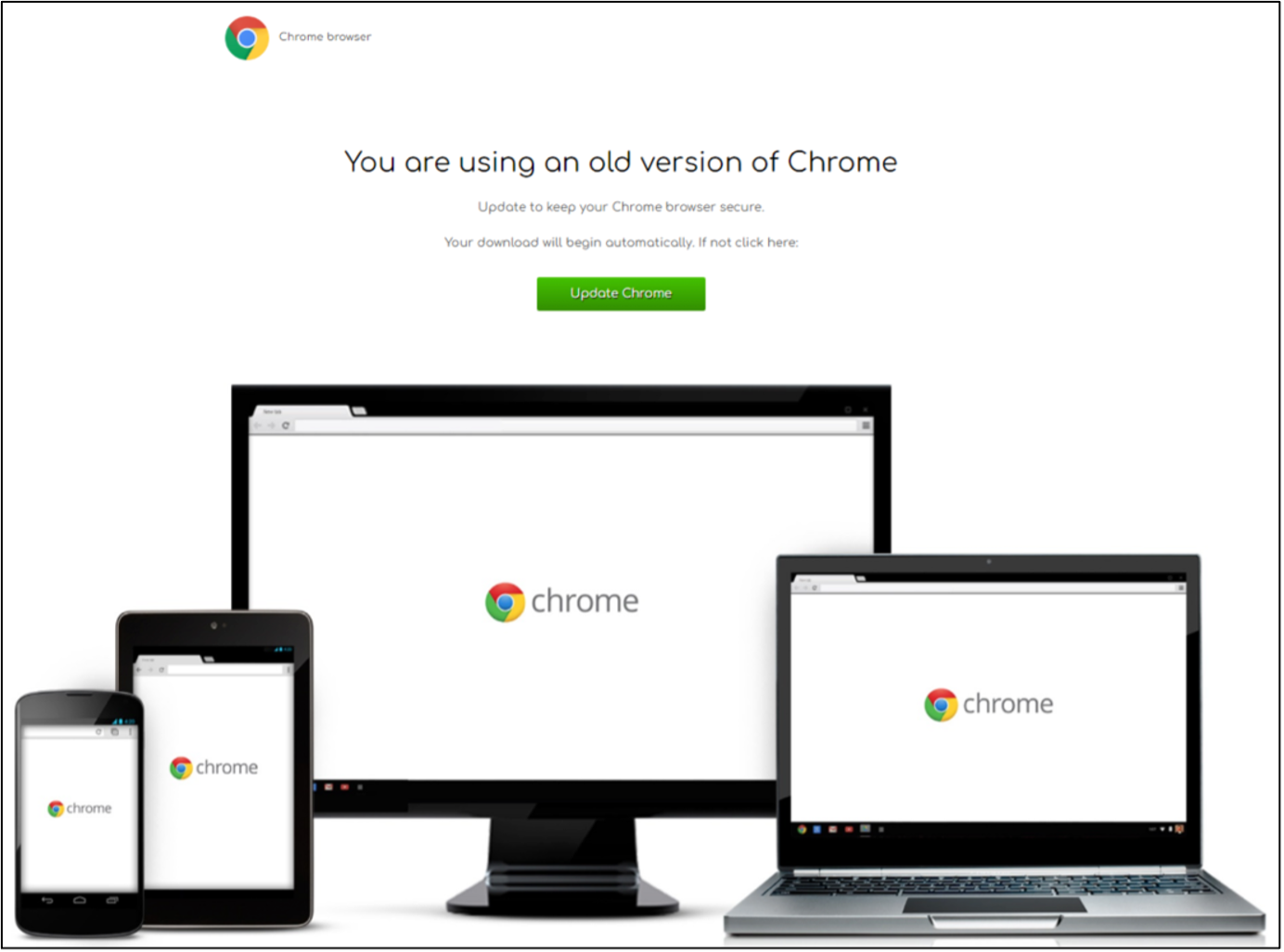
Figure 7. Example ZPHP lure spoofing a Chrome update.
![]()
Figure 8. Example ZPHP inject.
Proofpoint does not currently attribute the ZPHP activity to an actor with a TA number designation.
ClearFake
In August 2023, third-party researchers published details on a fake browser update threat activity known as ClearFake. Proofpoint subsequently identified consistent campaigns related to this cluster and observed a series of changes in the short amount of time while monitoring it. The inject is a base64 encoded script added to the HTML of the compromised webpage. Proofpoint observed the injection pointing to a variety of services including Cloudflare Workers, a file hosted on an actor’s GitHub, and most recently the blockchain network known as Binance Smart Chain. The initial request directs traffic to a stage 2 domain that hosts the Keitaro TDS filtering service to filter requests. The actor uses newly registered stage 2 domains, which, if a visitor passes the filtering, create an iFrame of the fake update lure hosted on the stage 2 domain. Clicking on the update button will result in a download of the payload which has been observed hosted on Dropbox and OneDrive.
The observed payload was either an executable (sometimes zipped), .msi, and .msix that leads to the installation of a variety of stealers including Lumma, Redline, and Raccoon v2.
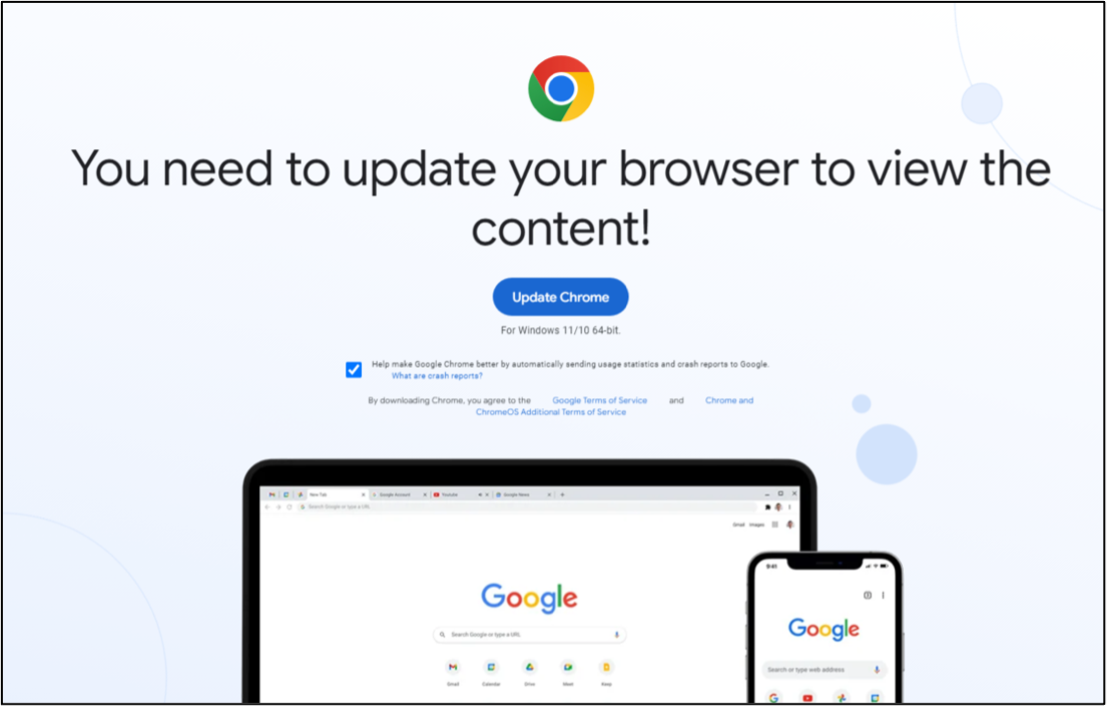
Figure 9. Example ClearFake lure spoofing a Chrome update.

Figure 10. Example ClearFake injection.
Notably, Proofpoint has observed ClearFake display the fake update lures in certain languages to match the browser's set language, including French, German, Spanish, and Portuguese. Proofpoint does not attribute the ClearFake activity to an actor with a TA number designation.
Conclusion
Proofpoint has observed an increase in threat activity using fake browser updates to deliver a variety of malware including payloads. SocGholish and TA569 have demonstrated that compromising vulnerable websites to display fake browser updates works as a viable method for malware delivery, and new actors have learned from TA569 and started to adopt the lure in their own ways. These copycats may be using information stealers and RATs currently, but could easily pivot to being an initial access broker for ransomware.
The activity detailed in this report can be hard for security teams to detect and prevent and may present difficulties with communicating the threat to end users due to the social engineering techniques and website compromises used by the threat actor. The best mitigation is defense in depth. Organizations should have network detections in place – including using the Emerging Threats ruleset – and use endpoint protection. Additionally, organizations should train users to identify the activity and report suspicious activity to their security teams. This is very specific training but can easily be integrated into an existing user training program. A tool such as Proofpoint’s Browser Isolation can also help prevent successful exploitation when compromised URLs are received via email and clicked on.
Specific indicators of compromise (IOCs) associated with the identified activities change regularly, as the threat actors are routinely moving their infrastructure and changing details in their payloads. The infosec.exchange account @monitorsg is a useful public resource for following along with recent details on payloads and infrastructure changes. The Emerging Threats Ruleset has domain rules available for most of the current threats and is regularly updating and publishing new rules to block all fake browser update campaigns.
Hunting IOCs and Payload Examples (As of 2023-09-28):
SocGholish:
C2 URI:
/editContent
8bdc4c1cd197808056e50b8b958acd380bf8a69b63aedef3f9854173c6714b32
3fb9740940d44eef823b7ff17f0274a12345a6f238cf46a1133a9e39c7b97c62
RogueRaticate:
Keitaro TDS Hosted on:
178.159.37.73
178.159.37.25
1d9900c8dbaa47d2587d08b334d483b06a39acb27f83223efc083759f1a7a4f6
08d9df800127f9fb7ff1a246346e1cf5cfef9a2521d40d6b2ab4e3614a19b772
ZPHP:
Injects lead to paths:
/cdn/wds.min.php
/cdn-js/wds.min.php
/cdn/zwmrqqgqnaww.php
/cdn/zwewmrqqgqnaww.php
e9580370160d39ef010dfdbfa614820cfe464507ce344a11bcbe760902297c8f
0b28e9df9daf8a3d0aa3dc8a066a34134916dfacd9ba5d25d78e097525f66492
ClearFake:
Chrome lure on:
/lander/chrome/_index.php
37bba90d20e429ce3fd56847e4e7aaf83c62fdd70a7dbdcd35b6f2569d47d533
ab282db6f1fc4b58272cef47522be19d453126b69f0e421da24487f54d611b2f
Emerging Threats Signatures: (All Open Sigs available for free)
“ET MALWARE SocGholish Domain in (DNS Lookup/TLS SNI) (<domain>)”
“ET MALWARE SocGholish CnC Domain in (DNS Lookup/TLS SNI) (<domain>)”
“ET EXPLOIT_KIT RogueRaticate Domain in (DNS Lookup/TLS SNI) (<domain>)”
“ET EXPLOIT_KIT Keitaro Set-Cookie Inbound to RogueRaticate (4cdcb)"
“ET EXPLOIT_KIT Keitaro Set-Cookie Inbound to RogueRaticate (3a7ee)"
“ET EXPLOIT_KIT Keitaro Set-Cookie Inbound to ClearFake (71eb8)”
“ET EXPLOIT_KIT ZPHP Domain in (DNS Lookup/TLS SNI) (<domain>)”











